Alcohol reversibly disrupts TNF-alpha/TACE interactions in the cell membrane
- PMID: 16246259
- PMCID: PMC1291403
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-123
Alcohol reversibly disrupts TNF-alpha/TACE interactions in the cell membrane
Abstract
Background: Alcohol abuse has long been known to adversely affect innate and adaptive immune responses and pre-dispose to infections. One cellular mechanism responsible for this effect is alcohol-induced suppression of TNF-alpha (TNF) by mononuclear phagocytes. We have previously shown that alcohol in part inhibits TNF-alpha processing by TNF converting enzyme (TACE) in human monocytes. We hypothesized that the chain length of the alcohol is critical for post-transcriptional suppression of TNF secretion.
Methods: Due to the complex transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of TNF in macrophages, to specifically study TNF processing at the cell membrane we performed transient transfections of A549 cells with the TNF cDNA driven by the heterologous CMV promoter. TNF/TACE interactions at the cell surface were assessed using fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscopy.
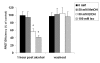
Results: The single carbon alcohol, methanol suppressed neither TNF secretion nor FRET efficiency between TNF and TACE. However, 2, 3, and 4 carbon alcohols were potent suppressors of TNF processing and FRET efficiency. The effect of ethanol, a 2-carbon alcohol was reversible.
Conclusion: These data show that inhibition of TNF-alpha processing by acute ethanol is a direct affect of ethanol on the cell membrane and is reversible upon cessation or metabolism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acute alcohol inhibits TNF-alpha processing in human monocytes by inhibiting TNF/TNF-alpha-converting enzyme interactions in the cell membrane.J Immunol. 2003 Mar 15;170(6):2923-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.6.2923. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12626543
-
Alcohol Decreases Organic Dust-Stimulated Airway Epithelial TNF-Alpha Through a Nitric Oxide and Protein Kinase-Mediated Inhibition of TACE.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Feb;40(2):273-83. doi: 10.1111/acer.12967. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 26842246 Free PMC article.
-
Microparticles of human atherosclerotic plaques enhance the shedding of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme/ADAM17 substrates, tumor necrosis factor and tumor necrosis factor receptor-1.Am J Pathol. 2007 Nov;171(5):1713-23. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070021. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17872973 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of TNF-alpha processing and TACE-mediated ectodomain shedding by ethanol.J Leukoc Biol. 2000 Jun;67(6):856-62. doi: 10.1002/jlb.67.6.856. J Leukoc Biol. 2000. PMID: 10857859
-
A Membrane Biophysics Perspective on the Mechanism of Alcohol Toxicity.Chem Res Toxicol. 2023 Jun 19;36(6):793-804. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.3c00039. Epub 2023 May 15. Chem Res Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37186813 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the role of TNF-α converting enzyme (TACE) in the inhibition of cell surface and soluble TNF-α production by acute ethanol exposure.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e29890. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029890. Epub 2012 Feb 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22319556 Free PMC article.
-
ELISA assays and alcohol: increasing carbon chain length can interfere with detection of cytokines.Alcohol. 2011 Feb;45(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2010.08.010. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Alcohol. 2011. PMID: 20843633 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling gene-by-environment interaction in comorbid depression with alcohol use disorders via an integrated bioinformatics approach.BioData Min. 2008 Jul 17;1(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1756-0381-1-2. BioData Min. 2008. PMID: 18822146 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Inhibits Organic Dust-induced ICAM-1 Expression on Bronchial Epithelial Cells.Safety (Basel). 2017 Mar;3(1):5. doi: 10.3390/safety3010005. Epub 2017 Jan 7. Safety (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29082234 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol exposure alters mouse lung inflammation in response to inhaled dust.Nutrients. 2012 Jul;4(7):695-710. doi: 10.3390/nu4070695. Epub 2012 Jul 4. Nutrients. 2012. PMID: 22852058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szabo G, Mandrekar P, Girouard L, Catalano D. Regulation of human monocyte functions by acute ethanol treatment: Decreased tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β and elevated interleukin-10, and transforming growth factor-β production. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20:900–907. - PubMed
-
- D'Souza NB, Bagby GJ, Nelson S, Lang CH, Spitzer JJ. Acute alcohol infusion suppressess endotoxin-induced tumor necrosis factor production. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1989;13:295–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

