Hydrolysis of angiotensin peptides by human angiotensin I-converting enzyme and the resensitization of B2 kinin receptors
- PMID: 16246972
- PMCID: PMC1564276
- DOI: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000188905.20884.63
Hydrolysis of angiotensin peptides by human angiotensin I-converting enzyme and the resensitization of B2 kinin receptors
Abstract
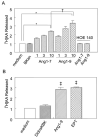
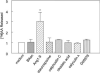
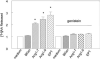
We measured the cleavage of angiotensin I (Ang I) metabolites by angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) in cultured cells and examined how they augment actions of bradykinin B2 receptor agonists. Monolayers of Chinese hamster ovary cells transfected to stably express human ACE and bradykinin B2 receptors coupled to green fluorescent protein (B2GFP) or to express only coupled B2GFP receptors. We used 2 ACE-resistant bradykinin analogues to activate the B2 receptors. We used high-performance liquid chromatography to analyze the peptides cleaved by ACE on cell monolayers and found that Ang 1-9 was hydrolyzed 18x slower than Ang I and &30% slower than Ang 1-7. Ang 1-7 was cleaved to Ang 1-5. Although micromol/L concentrations of slowly cleaved substrates Ang 1-7 and Ang 1-9 inhibit ACE, they resensitize the desensitized B2GFP receptors in nmol/L concentration, independent of ACE inhibition. This is reflected by release of arachidonic acid through a mechanism involving cross-talk between ACE and B2 receptors. When ACE was not expressed, the Ang 1-9, Ang 1-7 peptides were inactive. Inhibitors of protein kinase C-alpha, phosphatases and Tyr-kinase blocked this resensitization activity, but not basal B2 activation by bradykinin. Ang 1-9 and Ang 1-7 enhance bradykinin activity, probably by acting as endogenous allosteric modifiers of the ACE and B2 receptor complex. Consequently, when ACE inhibitors block conversion of Ang I, other enzymes can still release Ang I metabolites to enhance the efficacy of ACE inhibitors.
Figures

References
-
- Gavras H, Brunner HR, Laragh JH, Sealey JE, Gavras I, Vukovich RA. An angiotensin converting-enzyme inhibitor to identify and treat vasoconstrictor and volume factors in hypertensive patients. N Engl J Med. 1974;291:817–821. - PubMed
-
- Gavras I, Gavras H. The role of ACE inhibition in heart failure. In: D'Orleans-Juste P, Plante GE, editors. ACE Inhibitors. Birkhauser-Verlag; Basel, Switzerland: 2001. pp. 71–79.
-
- Yang HYT, Erdös EG, Levin Y. Characterization of a dipeptide hydrolase (kininase II; angiotensin I converting enzyme) J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971;177:291–300. - PubMed
-
- Gainer JV, Morrow JD, Loveland A, King DJ, Brown NJ. Effect of bradykinin-receptor blockade on the response to angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1285–1292. - PubMed
-
- Gafford JT, Skidgel RA, Erdös EG, Hersh LB. Human kidney “enkephalinase,” a neutral metalloendopeptidase that cleaves active peptides. Biochemistry. 1983;22:3265–3271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL068580-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL036473-17/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068580-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL36473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL036473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068580-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL68580/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL036473-18/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL036473-19/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL036473-20/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068580/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068580-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

