Concomitant loss of dynorphin, NARP, and orexin in narcolepsy
- PMID: 16247044
- PMCID: PMC2254145
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000168173.71940.ab
Concomitant loss of dynorphin, NARP, and orexin in narcolepsy
Abstract
Background: Narcolepsy with cataplexy is associated with a loss of orexin/hypocretin. It is speculated that an autoimmune process kills the orexin-producing neurons, but these cells may survive yet fail to produce orexin.
Objective: To examine whether other markers of the orexin neurons are lost in narcolepsy with cataplexy.
Methods: We used immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization to examine the expression of orexin, neuronal activity-regulated pentraxin (NARP), and prodynorphin in hypothalami from five control and two narcoleptic individuals.
Results: In the control hypothalami, at least 80% of the orexin-producing neurons also contained prodynorphin mRNA and NARP. In the patients with narcolepsy, the number of cells producing these markers was reduced to about 5 to 10% of normal.
Conclusions: Narcolepsy with cataplexy is likely caused by a loss of the orexin-producing neurons. In addition, loss of dynorphin and neuronal activity-regulated pentraxin may contribute to the symptoms of narcolepsy.
Figures
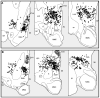
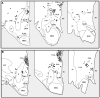
Comment in
-
Narcolepsy: selective hypocretin (orexin) neuronal loss and multiple signaling deficiencies.Neurology. 2005 Oct 25;65(8):1152-3. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000186118.96509.94. Neurology. 2005. PMID: 16247037 No abstract available.
References
-
- Peyron C, Faraco J, Rogers W, et al. A mutation in a case of early onset narcolepsy and a generalized absence of hypocretin peptides in human narcoleptic brains. Nature Medicine. 2000;6(9):991–997. - PubMed
-
- Mignot E, Lammers G, Ripley B, et al. The role of cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin measurement in the diagnosis of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias. Arch Neurol. 2002;59(10):1553–1562. - PubMed
-
- Chabas D, Taheri S, Renier C, Mignot E. The genetics of narcolepsy. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2003;4:459–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
