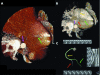
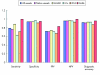
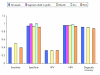
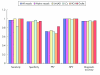
Non-invasive half millimetre 32 detector row computed tomography angiography accurately excludes significant stenoses in patients with advanced coronary artery disease and high calcium scores
- PMID: 16251224
- PMCID: PMC1860949
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2005.074336
Non-invasive half millimetre 32 detector row computed tomography angiography accurately excludes significant stenoses in patients with advanced coronary artery disease and high calcium scores
Abstract
Objective: To show an overall diagnostic accuracy > or = 90% for detection of > or = 50% stenoses by coronary half millimetre 32 detector row computed tomography angiography (32 x 0.5-MDCTA) in patients with advanced coronary artery disease (CAD) and a high likelihood of raised calcium scores.
Methods: ECG gated 32 x 0.5-MDCTA (32 x 0.5 mm cross sections, 0.35 x 0.35 x 0.35 mm3 isotropic voxels, 400 ms rotation) was performed after injection of iodixanol (120 ml, 320 mg/ml) in 30 consecutive patients (25 men, mean (SD) age 59 (13) years, body mass index 26.2 (4.9) kg/m2). Native arteries, including > or = 1.5 mm branches, and bypass grafts were screened for > or = 50% stenoses. Stents were excluded. Conventional coronary angiography (performed 18 (12) days before 32 x 0.5-MDCTA) was analysed by quantitative coronary angiography.
Results: Median Agatston calcium score was 510 (range 3-5066). Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for detection of > or = 50% stenoses in native arteries were 76% (29 of 38), 94% (190 of 202), 71% (29 of 41), and 96% (190 of 199), respectively. Overall diagnostic accuracy was 91% (219 of 240). Due to the following artefacts 20% (69 of 352) of the vessels were excluded: motion, noise, and low contrast enhancement isolated or in combination (45 of 69 (65%)); image distortion by implantable cardioverter-defibrillator or pacemaker leads (18 of 69 (26%)); and blooming secondary to severe calcification (6 of 69 (9%)).
Conclusions: Coronary 32 x 0.5-MDCTA accurately excludes > or = 50% stenoses in patients with advanced CAD and high calcium scores with an overall diagnostic accuracy of 91%.
Comment in
-
Computed tomographic coronary angiography: how many slices do you need?Heart. 2006 May;92(5):582-4. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2005.082198. Heart. 2006. PMID: 16614268 Free PMC article.
-
Can 32-detector-row CT exclude significant stenoses in coronary artery disease patients with high calcium scores?Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2006 Oct;3(10):534-5. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio0674. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2006. PMID: 16990836 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous