Regulation of the Caenorhabditis elegans oxidative stress defense protein SKN-1 by glycogen synthase kinase-3
- PMID: 16251270
- PMCID: PMC1283458
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508105102
Regulation of the Caenorhabditis elegans oxidative stress defense protein SKN-1 by glycogen synthase kinase-3
Abstract
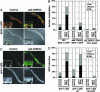
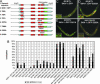
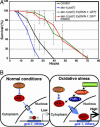
Oxidative stress plays a central role in many human diseases and in aging. In Caenorhabditis elegans the SKN-1 protein induces phase II detoxification gene transcription, a conserved oxidative stress response, and is required for oxidative stress resistance and longevity. Oxidative stress induces SKN-1 to accumulate in intestinal nuclei, depending on p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Here we show that, in the absence of stress, phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) prevents SKN-1 from accumulating in nuclei and functioning constitutively in the intestine. GSK-3 sites are conserved in mammalian SKN-1 orthologs, indicating that this level of regulation may be conserved. If inhibition by GSK-3 is blocked, background levels of p38 signaling are still required for SKN-1 function. WT and constitutively nuclear SKN-1 comparably rescue the skn-1 oxidative stress sensitivity, suggesting that an inducible phase II response may provide optimal stress protection. We conclude that (i) GSK-3 inhibits SKN-1 activity in the intestine, (ii) the phase II response integrates multiple regulatory signals, and (iii), by inhibiting this response, GSK-3 may influence redox conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Brownlee, M. (2001) Nature 414, 813-820. - PubMed
-
- Sheetz, M. J. & King, G. L. (2002) J. Am. Med. Assoc. 288, 2579-2588. - PubMed
-
- Droge, W. (2002) Physiol. Rev. 82, 47-95. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, J. K. (2004) Nat. Med. 10, S18-S25. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, R. S., Nemoto, S. & Finkel, T. (2005) Cell 120, 483-495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

