Regulation of RNA splicing by the methylation-dependent transcriptional repressor methyl-CpG binding protein 2
- PMID: 16251272
- PMCID: PMC1266160
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507856102
Regulation of RNA splicing by the methylation-dependent transcriptional repressor methyl-CpG binding protein 2
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jan 31;103(5):1656
Abstract
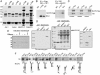
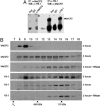
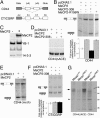
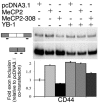
Rett syndrome (RTT) is a postnatal neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by the loss of acquired motor and language skills, autistic features, and unusual stereotyped movements. RTT is caused by mutations in the X-linked gene encoding methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2). Mutations in MECP2 cause a variety of neurodevelopmental disorders including X-linked mental retardation, psychiatric disorders, and some cases of autism. Although MeCP2 was identified as a methylation-dependent transcriptional repressor, transcriptional profiling of RNAs from mice lacking MeCP2 did not reveal significant gene expression changes, suggesting that MeCP2 does not simply function as a global repressor. Changes in expression of a few genes have been observed, but these alterations do not explain the full spectrum of Rett-like phenotypes, raising the possibility that additional MeCP2 functions play a role in pathogenesis. In this study, we show that MeCP2 interacts with the RNA-binding protein Y box-binding protein 1 and regulates splicing of reporter minigenes. Importantly, we found aberrant alternative splicing patterns in a mouse model of RTT. Thus, we uncovered a previously uncharacterized function of MeCP2 that involves regulation of splicing, in addition to its role as a transcriptional repressor.
Figures
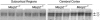
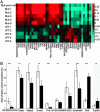
References
-
- Hagberg, B., Aicardi, J., Dias, K. & Ramos, O. (1983) Ann. Neurol., 14, 471–479. - PubMed
-
- Rett, A. (1966) Wien. Med. Wochenschr., 116, 723–726. - PubMed
-
- Einspieler, C., Kerr, A. M. & Prechtl, H. F. (2004) Pediatr. Res., 57, 696–700. - PubMed
-
- Neul, J. L. & Zoghbi, H. Y. (2004) Neuroscientist 10, 118–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

