Visualization of vacuolar acidification-induced transcription of genes of pathogens inside macrophages
- PMID: 16251362
- PMCID: PMC1345685
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1096
Visualization of vacuolar acidification-induced transcription of genes of pathogens inside macrophages
Abstract
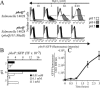
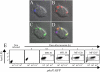
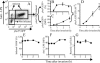
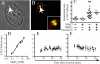
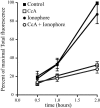
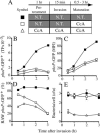
The objective of these studies was to analyze the role of the ionic environment of phagosomal vacuoles in the control of pathogens by macrophages. Digital imaging and flow cytometry were used to follow the induction of the phoP promoter of Salmonella enterica Typhimurium within live macrophages. Manipulating the Mg2+ concentration within the Salmonella-containing vacuole (SCV) was without effect on the early induction of PhoPQ. Moreover, direct measurement of [Mg2+] within the SCV using nanosensor particles showed that, during this initial period of phoP activation, the concentration of the divalent cation is rapidly regulated and stabilizes around 1 mm. Extrusion of other divalent cations via the Nramp1 efflux pump was similarly ruled out as an important contributor to the activation of the regulon. By contrast, induction of PhoP was greatly attenuated when the pH gradient across the SCV membrane was dissipated. A second, more modest pH-independent component of PhoP induction was unmasked by inhibition of the vacuolar proton pump. This second component was eliminated by pretreatment of cells with IFNgamma, even though the cytokine augmented the overall PhoP response. These findings demonstrate the existence of at least three separate activators of phoP transcription: resting and IFNgamma-stimulated pH-sensitive components, plus a pH-independent component.
Figures
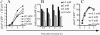
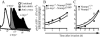
Similar articles
-
Salmonella typhimurium activates virulence gene transcription within acidified macrophage phagosomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10079-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10079. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. PMID: 1438196 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between MgtC and PagC in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Microb Pathog. 2008 Sep;45(3):236-40. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2008.06.001. Epub 2008 Jun 24. Microb Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18620040
-
Contribution of the PhoP/Q regulon to survival and replication of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in macrophages.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Jul;157(Pt 7):2084-2093. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.048926-0. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 21511762 Free PMC article.
-
How Pathogens Feel and Overcome Magnesium Limitation When in Host Tissues.Trends Microbiol. 2021 Feb;29(2):98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Trends Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 32807623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maturation steps of the Salmonella-containing vacuole.Microbes Infect. 2001 Nov-Dec;3(14-15):1299-303. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01490-3. Microbes Infect. 2001. PMID: 11755418 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome expression analysis of nonproliferating intracellular Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium unravels an acid pH-dependent PhoP-PhoQ response essential for dormancy.Infect Immun. 2013 Jan;81(1):154-65. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01080-12. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23090959 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular DNA-induced antimicrobial peptide resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.BMC Microbiol. 2013 May 24;13:115. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-115. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23705831 Free PMC article.
-
Replication of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium in Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages.Infect Immun. 2015 Jul;83(7):2661-71. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00033-15. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25895967 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of phagosome trafficking and identification of PhoP-regulated genes important for survival of Yersinia pestis in macrophages.Infect Immun. 2006 Jul;74(7):3727-41. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00255-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16790745 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated circuits: how transcriptional silencing and counter-silencing facilitate bacterial evolution.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Feb;23:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25461567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amer, A. O., and Swanson, M. S. (2002). A phagosome of one's own: a microbial guide to life in the macrophage. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 5, 56-61. - PubMed
-
- Bader, M. W., Navarre, W. W., Shiau, W., Nikaido, H., Frye, J. G., McClelland, M., Fang, F. C., and Miller, S. I. (2003). Regulation of Salmonella typhimurium virulence gene expression by cationic antimicrobial peptides. Mol. Microbiol. 50, 219-230. - PubMed
-
- Bader, M. W., Sanowar, S., Daley, M. E., Schneider, A. R., Cho, U., Xu, W., Klevit, R. E., Le Moual, H., and Miller, S. I. (2005). Recognition of antimicrobial peptides by a bacterial sensor kinase. Cell 122, 461-472. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

