Characteristics and regulatory elements defining constitutive splicing and different modes of alternative splicing in human and mouse
- PMID: 16251388
- PMCID: PMC1370866
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2660805
Characteristics and regulatory elements defining constitutive splicing and different modes of alternative splicing in human and mouse
Abstract
Alternative splicing is a major contributor to genomic complexity, disease, and development. Previous studies have captured some of the characteristics that distinguish alternative splicing from constitutive splicing. However, most published work only focuses on skipped exons and/or a single species. Here we take advantage of the highly curated data in the MAASE database (see related paper in this issue) to analyze features that characterize different modes of splicing. Our analysis confirms previous observations about alternative splicing, including weaker splicing signals at alternative splice sites, higher sequence conservation surrounding orthologous alternative exons, shorter exon length, and more frequent reading frame maintenance in skipped exons. In addition, our study reveals potentially novel regulatory principles underlying distinct modes of alternative splicing and a role of a specific class of repeat elements (transposons) in the origin/evolution of alternative exons. These features suggest diverse regulatory mechanisms and evolutionary paths for different modes of alternative splicing.
Figures
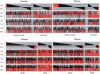
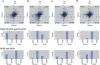

References
-
- Baelde, H.J., Eikmans, M., Doran, P.P., Lappin, D.W., de Heer, E., and Bruijn, J.A. 2004a. Gene expression profiling in glomeruli from human kidneys with diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 43: 636–650. - PubMed
-
- Baelde, H.J., Eikmans, M., van Vliet, A.I., Bergijk, E.C., de Heer, E., and Bruijn, J.A. 2004b. Alternatively spliced isoforms of fibronectin in immune-mediated glomerulosclerosis: The role of TGFβ and IL-4. J. Pathol. 204: 248–257. - PubMed
-
- Berget, S.M. 1995. Exon recognition in vertebrate splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 2411–2414. - PubMed
-
- Brett, D., Pospisil, H., Valcarcel, J., Reich, J., and Bork, P. 2002. Alternative splicing and genome complexity. Nat. Genet. 30: 29–30. - PubMed
-
- Caceres, J.F. and Kornblihtt, A.R. 2002. Alternative splicing: Multiple control mechanisms and involvement in human disease. Trends Genet. 18: 186–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
