Stromal regulation of neoplastic development: age-dependent normalization of neoplastic mammary cells by mammary stroma
- PMID: 16251424
- PMCID: PMC1603788
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61227-8
Stromal regulation of neoplastic development: age-dependent normalization of neoplastic mammary cells by mammary stroma
Abstract
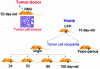
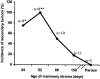
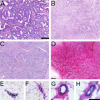
There is mounting evidence that the stroma plays a crucial role in mammary gland carcinogenesis. Here, we report that mammary gland stroma from mature and multiparous rats prevents neoplastic development and encourages normal ductal growth of grafted epithelial cancer cells. Fifty thousand epithelial cancer cells were injected into the cleared fat pads of virgin hosts at 24, 52, 80, and 150 days of age and of hosts that had undergone two cycles of pregnancy, lactation, and involution. Six months after inoculation, tumor incidence was 75%, 100%, 50%, and 18.2% in 24-, 52-, 80-, and 150-day-old virgin rats, respectively, and 0% in the twice-parous animals. Most remarkably, these neoplastic cells appeared to form normal ducts in all hosts-Ha-ras-1 mutation served as a marker to identify the tumor origin of the outgrowths. The tumor development pattern suggests a parallel to the phenomenon of age- and reproductive state-dependent susceptibility and resistance to chemical carcinogens. As susceptibility to carcinogenesis decreases, the ability of the stroma to reprogram neoplastic epithelial cells increases. Thus, the neoplastic phenotype is context-dependent, and it therefore offers the intriguing possibility that the process of carcinogenesis is amenable to normalization or cure once the mechanisms of stroma-mediated normalization are elucidated and manipulated.
Figures

References
-
- Gilbert SF. Proximate tissue interactions: secondary induction. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates, Inc.,; Developmental Biology. (ed 3) 1991:pp 570–606.
-
- Shekhar MP, Werdell J, Santner SJ, Pauley RJ, Tait L. Breast stroma plays a dominant regulatory role in breast epithelial growth and differentiation: implications for tumor development and progression. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1320–1326. - PubMed
-
- Cunha GR, Hayward SW, Wang YZ, Ricke WA. Role of the stromal microenvironment in carcinogenesis of the prostate. Int J Cancer. 2003;107:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Cunha GR, Bigsby RM, Cooke PS, Sugimura Y. Stromal-epithelial interactions in adult organs. Cell Differ. 1985;17:137–148. - PubMed
-
- Potter J. Morphostats: a missing concept in cancer biology. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001;10:167–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

