Regulation of Kv7 (KCNQ) K+ channel open probability by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
- PMID: 16251430
- PMCID: PMC6725574
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2597-05.2005
Regulation of Kv7 (KCNQ) K+ channel open probability by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Abstract
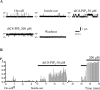
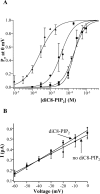
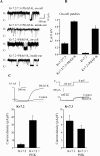
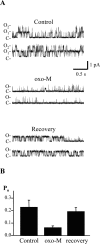
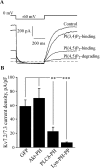
Voltage-gated Kv7 (KCNQ) channels underlie important K+ currents, including the neuronal M current, and are thought to be sensitive to membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) and PIP2 depletion to underlie muscarinic receptor inhibition. We studied regulation of Kv7.2-7.4 channels by PIP2 in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells using single-channel and whole-cell patch clamp and biochemical analysis. Maximal open probabilities (Po) of Kv7.2-Kv7.4 homomultimers and of Kv7.2/7.3 heteromultimers were found to be strongly dependent on the [diC8-PIP2] applied to inside-out patches, with differential apparent affinities that correlate with their maximal Po in on-cell mode. Unitary conductance was not affected by PIP2. Raising tonic [PIP2] by coexpression of phosphatidylinositol (4)5-kinase increased the maximal Po of both Kv7.2 and Kv7.2/7.3 channels studied in on-cell patches and increased whole-cell Kv7.2, but not Kv7.3, current amplitudes. In cells coexpressed with muscarinic M1 receptors, bath application of muscarinic agonist reduced the maximal Po of Kv7.2/7.3 channels isolated in on-cell patches. Coexpression of a PIP2 sequestering construct moderately reduced whole-cell Kv7.2/7.3 currents, and coexpression of a construct containing a PIP2 phosphatase nearly abolished them. Finally, biochemical analysis of anionic phospholipids in CHO cells stably expressing M1 receptors shows that PIP2 and PIP are nearly depleted 1 min after muscarinic stimulation, with an unexpected rebound after 10 min. These results strongly support the direct regulation of Kv7 channels by PIP2 and its depletion as the mechanism of muscarinic suppression of M channels. Divergent apparent affinities of Kv7.2-7.4 channels for PIP2 may underlie their highly differential maximal Po observed in cell-attached patches.
Figures


References
-
- Bender K, Wellner-Kienitz MC, Pott L (2002) Transfection of a phosphatidyl-4-phosphate 5-kinase gene into rat atrial myocytes removes inhibition of GIRK current by endothelin and alpha-adrenergic agonists. FEBS Lett 529: 356-360. - PubMed
-
- Bofill-Cardona E, Vartian N, Nanoff C, Freissmuth M, Boehm S (2000) Two different signaling mechanisms involved in the excitation of rat sympathetic neurons by uridine nucleotides. Mol Pharmacol 57: 1165-1172. - PubMed
-
- Delmas P, Brown DA (2005) Pathways modulating neural KCNQ/M (Kv7) potassium channels. Nat Rev Neurosci, in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
