Role of hippocampal Cav1.2 Ca2+ channels in NMDA receptor-independent synaptic plasticity and spatial memory
- PMID: 16251435
- PMCID: PMC6725564
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1531-05.2005
Role of hippocampal Cav1.2 Ca2+ channels in NMDA receptor-independent synaptic plasticity and spatial memory
Abstract
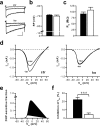
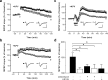
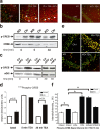
Current knowledge about the molecular mechanisms of NMDA receptor (NMDAR)-independent long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus and its function for memory formation in the behaving animal is limited. NMDAR-independent LTP in the CA1 region is thought to require activity of postsynaptic L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels (Cav1.x), but the underlying channel isoform remains unknown. We evaluated the function of the Cav1.2 L-type Ca2+ channel for spatial learning, synaptic plasticity, and triggering of learning-associated biochemical processes using a mouse line with an inactivation of the CACNA1C (Cav1.2) gene in the hippocampus and neocortex (Cav1.2(HCKO)). This model shows (1) a selective loss of protein synthesis-dependent NMDAR-independent Schaffer collateral/CA1 late-phase LTP (L-LTP), (2) a severe impairment of hippocampus-dependent spatial memory, and (3) decreased activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and reduced cAMP response element (CRE)-dependent transcription in CA1 pyramidal neurons. Our results provide strong evidence for a role of L-type Ca2+ channel-dependent, NMDAR-independent hippocampal L-LTP in the formation of spatial memory in the behaving animal and for a function of the MAPK/CREB (CRE-binding protein) signaling cascade in linking Cav1.2 channel-mediated Ca2+ influx to either process.
Figures



References
-
- Adelsberger H, Tsien J, Konnerth A (2005) Superior learning abilities of NR2B transgenic mice in a new labyrinth task. In: Proceedings of the 6th Meeting of the German Neuroscience Society (Krieglstein K, ed), p 244B. Berlin: Neurowissenschaftliche Gesellschaft.
-
- Aizawa H, Hu SC, Bobb K, Balakrishnan K, Ince G, Gurevich I, Cowan M, Ghosh A (2004) Dendrite development regulated by CREST, a calcium-regulated transcriptional activator. Science 303: 197-202. - PubMed
-
- Aniksztejn L, Ben-Ari Y (1991) Novel form of long-term potentiation produced by a K+ channel blocker in the hippocampus. Nature 349: 67-69. - PubMed
-
- Arns M, Sauvage M, Steckler T (1999) Excitotoxic hippocampal lesions disrupt allocentric spatial learning in mice: effects of strain and task demands. Behav Brain Res 106: 151-164. - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD (1998) The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci 1: 602-609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
