In vivo magnetic resonance microimaging of individual amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's transgenic mice
- PMID: 16251453
- PMCID: PMC2744887
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2588-05.2005
In vivo magnetic resonance microimaging of individual amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's transgenic mice
Abstract
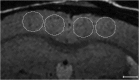
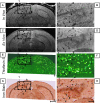
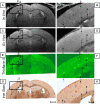
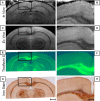
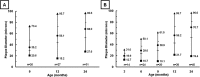
The ability to detect individual Alzheimer's amyloid plaques in vivo by magnetic resonance microimaging (MRI) should improve diagnosis and also accelerate discovery of effective therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here, we perform in vivo and ex vivo MRI on double transgenic AD mice as well as wild-type mice at varying ages and correlate these with thioflavin-S and iron staining histology. Quantitative counts of individual plaques on MRI increase with age and correlate with histologically determined plaque burden. Plaques 20 microm in diameter can be detected in AD mice as young as 3 months of age with ex vivo MRI. Plaques 35 microm in diameter can be detected by 9 months of age with in vivo MRI. In vivo MRI of individual Alzheimer's amyloid plaques provides a noninvasive estimate of plaque burden in transgenic AD mice that might be useful in assessing the efficacy of amyloid reduction therapies.
Figures




References
-
- Dhenain M, Privat N, Duyckaerts C, Jacobs RE (2002) Senile plaques do not induce susceptibility effects in T2*-weighted MR microscopic images. NMR Biomed 15: 197-203. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297: 353-356. - PubMed
-
- Helpern JA, Lee S-P, Falangola MF, Dyakin V, Bogart A, Ardekani B, Duff K, Branch C, Wisniewski T, de Leon MJ, Wolf O, O'Shea J, Nixon RA (2004) MRI assessment of neuropathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Magn Reson Med 51: 794-798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
