Mapping determinants of human gene expression by regional and genome-wide association
- PMID: 16251966
- PMCID: PMC3005311
- DOI: 10.1038/nature04244
Mapping determinants of human gene expression by regional and genome-wide association
Abstract
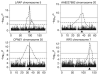
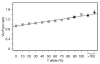
To study the genetic basis of natural variation in gene expression, we previously carried out genome-wide linkage analysis and mapped the determinants of approximately 1,000 expression phenotypes. In the present study, we carried out association analysis with dense sets of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers from the International HapMap Project. For 374 phenotypes, the association study was performed with markers only from regions with strong linkage evidence; these regions all mapped close to the expressed gene. For a subset of 27 phenotypes, analysis of genome-wide association was performed with >770,000 markers. The association analysis with markers under the linkage peaks confirmed the linkage results and narrowed the candidate regulatory regions for many phenotypes with strong linkage evidence. The genome-wide association analysis yielded highly significant results that point to the same locations as the genome scans for about 50% of the phenotypes. For one candidate determinant, we carried out functional analyses and confirmed the variation in cis-acting regulatory activity. Our findings suggest that association studies with dense SNP maps will identify susceptibility loci or other determinants for some complex traits or diseases.
Figures

References
-
- International HapMap Consortium The International HapMap Project. Nature. 2003;426:789–796. - PubMed
-
- Cheung VG, Spielman RS. The genetics of variation in gene expression. Nature Genet. 2002;32:522–525. - PubMed
-
- Cheung VG, et al. Natural variation in human gene expression assessed in ymphoblastoid cells. Nature Genet. 2003;33:422–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

