New frontiers in radiosurgery for the brain and body
- PMID: 16252020
- PMCID: PMC1255939
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2005.11928087
New frontiers in radiosurgery for the brain and body
Abstract
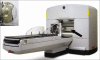
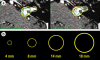
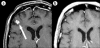
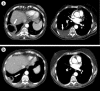
Radiosurgery is defined as the use of highly focused beams of radiation to ablate a pathologic target, thus achieving a surgical objective by noninvasive means. Recent advances have allowed a wide variety of intracranial lesions to be effectively treated with radiosurgery, and radiosurgical treatment has been accepted as a standard part of the neurosurgical armamentarium. The advent of frameless radiosurgery now permits radiosurgical treatment to all parts of the body and is being actively explored by many centers. This article reviews some of the modern tools for radiosurgical treatment and discusses the current clinical practice of radiosurgery.
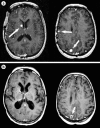
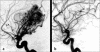
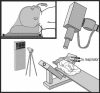
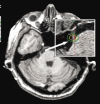
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regarding: Rosenthal DI, Glatstein E. "We've Got a Treatment, but What's the Disease?" The Oncologist 1996;1.Oncologist. 1997;2(1):59-61. Oncologist. 1997. PMID: 10388030
-
CyberKnife radiosurgery for brain metastases.Prog Neurol Surg. 2012;25:201-9. doi: 10.1159/000331193. Epub 2012 Jan 6. Prog Neurol Surg. 2012. PMID: 22236681 Review.
-
Current status and optimal use of radiosurgery.Oncology (Williston Park). 2001 Feb;15(2):209-16; discussion 219-21. Oncology (Williston Park). 2001. PMID: 11252934 Review.
-
Frame versus Frameless Leksell Stereotactic Radiosurgery.Prog Neurol Surg. 2019;34:19-27. doi: 10.1159/000493046. Epub 2019 May 16. Prog Neurol Surg. 2019. PMID: 31096212 Review.
-
CyberKnife frameless stereotactic radiosurgery for spinal lesions: clinical experience in 125 cases.Neurosurgery. 2004 Jul;55(1):89-98; discussion 98-9. Neurosurgery. 2004. PMID: 15214977 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
A lipoxygenase inhibitor in breast cancer brain metastases.J Neurooncol. 2007 Mar;82(1):91-3. doi: 10.1007/s11060-006-9248-4. Epub 2006 Sep 26. J Neurooncol. 2007. PMID: 17001517
-
Conventionally-fractionated image-guided intensity modulated radiotherapy (IG-IMRT): a safe and effective treatment for cancer spinal metastasis.Radiat Oncol. 2008 Apr 22;3:11. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-3-11. Radiat Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18426607 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation of intrafraction motion and overall geometrical accuracy of a frameless intracranial radiosurgery process.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2008 Oct 24;9(4):68-86. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v9i4.2828. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 19020489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leksell L. Stereotaxis and Radiosurgery. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas; 1971.
-
- Mack A, Czempiel H, Kreiner HJ, Durr G, Wowra B. Quality assurance in stereotactic space. A system test for verifying the accuracy of aim in radiosurgery. Med Phys. 2002;29:561–568. - PubMed
-
- Adler JR, Murphy MJ, Chang SD, Hancock SL. Image-guided robotic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 1999;44:1299–1307. - PubMed
-
- Kuo JS, Yu C, Petrovich Z, Apuzzo ML. The CyberKnife stereotactic radiosurgery system: description, installation, and an initial evaluation of use and functionality. Neurosurgery. 2003;53:1235–1239. - PubMed
-
- Chang SD, Main W, Martin DP, Gibbs IC, Heilbrun MP. An analysis of the accuracy of the CyberKnife: a robotic frameless stereotactic radiosurgical system. Neurosurgery. 2003;52:140–146. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
