Rat bite fever caused by Streptobacillus moniliformis in a child: human infection and rat carriage diagnosed by PCR
- PMID: 16254115
- PMCID: PMC1770754
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2005.026401
Rat bite fever caused by Streptobacillus moniliformis in a child: human infection and rat carriage diagnosed by PCR
Abstract
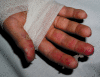
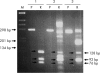
A child owning pet rats developed an eruptive fever with blisters, polyarthritis, and spectacular desquamation of the hands. Streptobacillus moniliformis was identified after culture of the child's blister fluid and was detected in rat samples by molecular methods. Such detection in the pet of a human victim of rat bite fever has not been reported previously.
Figures
References
-
- Boot R, Oosterhuis A, Thuis HC. PCR for the detection of Streptobacillus moniliformis. Lab Anim 2002;36:200–8. - PubMed
-
- Denizot MJ, Hansen W, Bollet C. Streptobacillus moniliformis. In: Freney J, Renaud F, Hansen W, et al, eds. Précis de bactériologie clinique. Paris, France: ESKA, 2000:1495–8.
-
- Hagelskjaer L, Sorensen I, Randers E. Streptobacillus moniliformis infection: 2 cases and a literature review. Scand J Infect Dis 1998;30:309–11. - PubMed
-
- Wallet F, Savage C, Loiez C, et al. Molecular diagnosis of arthritis due to Streptobacillus moniliformis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2003;47:623–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
