Proinflammatory effects of bacterial recombinant human C-reactive protein are caused by contamination with bacterial products, not by C-reactive protein itself
- PMID: 16254214
- PMCID: PMC1400607
- DOI: 10.1161/01.RES.0000193595.03608.08
Proinflammatory effects of bacterial recombinant human C-reactive protein are caused by contamination with bacterial products, not by C-reactive protein itself
Abstract
Intravenous administration to human volunteers of a commercial preparation of recombinant human C-reactive protein (CRP) produced in Escherichia coli was recently reported in this journal to induce an acute phase response of serum amyloid A protein (SAA) and of CRP itself, and to activate the coagulation system. The authors concluded that CRP is probably a mediator of atherothrombotic disease. Here we confirm that this recombinant CRP preparation was proinflammatory both for mouse macrophages in vitro and for mice in vivo, but show that pure natural human CRP had no such activity. Furthermore mice transgenic for human CRP, and expressing it throughout their lives, maintained normal concentrations of their most sensitive endogenous acute phase reactants, SAA and serum amyloid P component (SAP). The patterns of in vitro cytokine induction and of in vivo acute phase stimulation by the recombinant CRP preparation were consistent with contamination by bacterial products, and there was 46.6 EU of apparent endotoxin activity per mg of CRP in the bacterial product, compared with 0.9 EU per mg of our isolated natural human CRP preparation. The absence of any proinflammatory activity in natural CRP for macrophages or healthy mice strongly suggests that the in vivo effects of the recombinant preparation observed in humans were attributable to proinflammatory bacterial products and not human CRP.
Figures
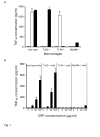
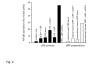
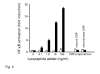
Comment in
-
In vivo effects of C-reactive protein (CRP)-infusion into humans.Circ Res. 2005 Dec 9;97(12):e115-6. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000196746.75724.8b. Circ Res. 2005. PMID: 16339489 No abstract available.
References
-
- Liuzzo G, Biasucci LM, Gallimore JR, Grillo RL, Rebuzzi AG, Pepys MB, Maseri A. The prognostic value of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A protein in severe unstable angina. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:417–424. - PubMed
-
- Pepys MB. C-reactive protein fifty years on. Lancet. 1981;i:653–656. - PubMed
-
- Kindmark C-O, Thorell JI. Quantitative determination of individual serum proteins by radio-electroimmunoassay and use of 125I-labelled antibodies (application to C-reactive protein) Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972;29(Suppl 124):49–53. - PubMed
-
- Shine B, de Beer FC, Pepys MB. Solid phase radioimmunoassays for human C-reactive protein. Clin Chim Acta. 1981;117:13–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

