Viral protein VP4 is a target of human antibodies enhancing coxsackievirus B4- and B3-induced synthesis of alpha interferon
- PMID: 16254324
- PMCID: PMC1280186
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.22.13882-13891.2005
Viral protein VP4 is a target of human antibodies enhancing coxsackievirus B4- and B3-induced synthesis of alpha interferon
Abstract
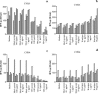
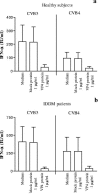
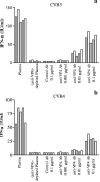
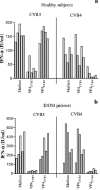
Coxsackievirus B4 (CVB4)-induced production of alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) is enhanced in vitro by nonneutralizing anti-CVB4 antibodies from healthy subjects and, to a higher extent, from patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. In this study, we focused on identification of the viral target of these antibodies in CVB systems. High levels of IFN-alpha were obtained in supernatants of PBMC incubated with CVB4E2 or CVB3 and plasma from healthy subjects and, to a higher extent, from patients. The VP4 capsid proteins dissociated by heating at 56 degrees C from CVB4E2 (VP4(CVB4)) and CVB3 (VP4(CVB3)) but not H antigen preincubated with plasma from healthy subjects or patients inhibited the plasma-dependent enhancement of CVB4E2- and CVB3-induced IFN-alpha synthesis. There was no cross-reaction between VP4(CVB4) and VP4(CVB3) in the inhibiting effect. IFN-alpha levels in culture supernatants showed dose-dependent correlation with anti-VP4 antibodies eluted from plasma specimens using VP4-coated plates. There were higher index values for anti-VP4 antibodies detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and higher proportions of positive detection in 40 patients than in 40 healthy subjects (80% versus 15% for anti-VP4(CVB4)). There was no relationship between the levels of anti-CVB neutralizing antibodies and the detection of anti-VP4 antibodies by ELISA. The CVB plasma-induced IFN-alpha levels obtained in PBMC cultures in the anti-VP4 antibody-positive groups were significantly higher than those obtained in the anti-VP4 antibody-negative groups regardless of the titers of anti-CVB neutralizing antibodies. These results show that VP4 is the target of antibodies involved in the plasma-dependent enhancement of CVB4E2- and CVB3-induced IFN-alpha synthesis by PBMC.
Figures


References
-
- Andreoletti, L., D. Hober, C. Hober-Vandenberghe, S. Belaich, M. C. Vantyghem, J. Lefebvre, and P. Wattre. 1997. Detection of coxsackie B virus RNA sequences in whole blood samples from adult patients at the onset of type I diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Virol. 52:121-127. - PubMed
-
- Bosi, E., R. Minelli, E. Bazzigaluppi, and M. Salvi. 2001. Fulminant autoimmune type 1 diabetes during interferon-alpha therapy: a case of Th1-mediated disease? Diabet. Med. 18:329-332. - PubMed
-
- Boyum, A. 1976. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand. J. Immunol. Suppl. 5:9-15. - PubMed
-
- Brahimi, K., J. L. Perignon, M. Bossus, H. Gras, A. Tartar, and P. Druilhe. 1993. Fast immunopurification of small amounts of specific antibodies on peptides bound to ELISA plates. J. Immunol. Methods 162:69-75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

