Posttranslational modification of alpha-dystroglycan, the cellular receptor for arenaviruses, by the glycosyltransferase LARGE is critical for virus binding
- PMID: 16254363
- PMCID: PMC1280193
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.22.14282-14296.2005
Posttranslational modification of alpha-dystroglycan, the cellular receptor for arenaviruses, by the glycosyltransferase LARGE is critical for virus binding
Abstract
The receptor for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), the human pathogenic Lassa fever virus (LFV), and clade C New World arenaviruses is alpha-dystroglycan (alpha-DG), a cell surface receptor for proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Specific posttranslational modification of alpha-DG by the glycosyltransferase LARGE is critical for its function as an ECM receptor. In the present study, we show that LARGE-dependent modification is also crucial for alpha-DG's function as a cellular receptor for arenaviruses. Virus binding involves the mucin-type domain of alpha-DG and depends on modification by LARGE. A crucial role of the LARGE-dependent glycosylation of alpha-DG for virus binding is found for several isolates of LCMV, LFV, and the arenaviruses Mobala and Oliveros. Since the posttranslational modification by LARGE is crucial for alpha-DG recognition by both arenaviruses and the host-derived ligand laminin, it also influences competition between virus and laminin for alpha-DG. Hence, LARGE-dependent glycosylation of alpha-DG has important implications for the virus-host cell interaction and the pathogenesis of LFV in humans.
Figures

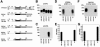

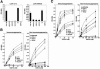



References
-
- Ahmed, R., A. Salmi, L. D. Butler, J. M. Chiller, and M. B. Oldstone. 1984. Selection of genetic variants of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in spleens of persistently infected mice. Role in suppression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and viral persistence. J. Exp. Med. 160:521-540. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barresi, R., D. E. Michele, M. Kanagawa, H. A. Harper, S. A. Dovicio, J. S. Satz, S. A. Moore, W. Zhang, H. Schachter, J. P. Dumanski, et al. 2004. LARGE can functionally bypass alpha-dystrolycan glycosylation defects in distinct congential muscular dystrophy. Nat. Med. 7:696-703. - PubMed
-
- Beltran-Valero de Bernabe, D., S. Currier, A. Steinbrecher, J. Celli, E. van Beusekom, B. van der Zwaag, H. Kayserili, L. Merlini, D. Chitayat, W. B. Dobyns, B. Cormand, A. E. Lehesjoki, J. Cruces, T. Voit, C. A. Walsh, H. van Bokhoven, and H. G. Brunner. 2002. Mutations in the O-mannosyltransferase gene POMT1 give rise to the severe neuronal migration disorder Walker-Warburg syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71:1033-1043. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

