Rabies virus P protein interacts with STAT1 and inhibits interferon signal transduction pathways
- PMID: 16254375
- PMCID: PMC1280226
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.22.14411-14420.2005
Rabies virus P protein interacts with STAT1 and inhibits interferon signal transduction pathways
Abstract
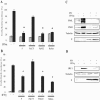
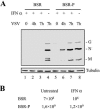
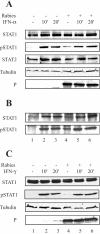
Rabies virus P protein is a cofactor of RNA polymerase. We investigated other potential roles of P (CVS strain) by searching for cellular partners using two-hybrid screening. We isolated a cDNA encoding the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) that is a critical component of interferon type I (IFN-alpha/beta) and type II (IFN-gamma) signaling. We confirmed this interaction by glutathione S-transferase-pull-down assay. Deletion mutant analysis indicated that the carboxy-terminal part of P interacted with a region containing the DNA-binding domain and the coiled-coil domain of STAT1. The expression of P protein inhibits IFN-alpha- and IFN-gamma-induced transcriptional responses, thus impairing the IFN-induced antiviral state. Mechanistic studies indicate that P protein does not induce STAT1 degradation and does not interfere with STAT1 phosphorylation but prevents IFN-induced STAT1 nuclear accumulation. These results indicate that rabies P protein overcomes the antiviral response of the infected cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The nucleocytoplasmic rabies virus P protein counteracts interferon signaling by inhibiting both nuclear accumulation and DNA binding of STAT1.J Virol. 2007 Apr;81(8):4255-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01930-06. Epub 2007 Feb 7. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17287281 Free PMC article.
-
Nipah virus V and W proteins have a common STAT1-binding domain yet inhibit STAT1 activation from the cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments, respectively.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(11):5633-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.11.5633-5641.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15140960 Free PMC article.
-
Measles virus V protein blocks Jak1-mediated phosphorylation of STAT1 to escape IFN-alpha/beta signaling.Virology. 2007 Nov 25;368(2):351-62. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.06.037. Epub 2007 Aug 7. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17686504
-
Interplay between interferon and other cytokine systems in bone metabolism.Immunol Rev. 2005 Dec;208:181-93. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00337.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16313349 Review.
-
Characterization of P gene-deficient rabies virus: propagation, pathogenicity and antigenicity.Virus Res. 2005 Jul;111(1):61-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.03.011. Epub 2005 Apr 11. Virus Res. 2005. PMID: 15896403 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic and evolutionary characterization of RABVs from China using the phosphoprotein gene.Virol J. 2013 Jan 7;10:14. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-14. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 23294868 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibilities of CNS Cells towards Rabies Virus Infection Is Linked to Cellular Innate Immune Responses.Viruses. 2022 Dec 29;15(1):88. doi: 10.3390/v15010088. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36680128 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of Functional Effects of Phosphorylation of the C-Terminal Domain of the Rabies Virus P Protein.J Virol. 2022 May 11;96(9):e0011122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00111-22. Epub 2022 Apr 11. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35404083 Free PMC article.
-
The cell biology of rabies virus: using stealth to reach the brain.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 Jan;8(1):51-61. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2260. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19946287 Review.
-
Involvement of the rabies virus phosphoprotein gene in neuroinvasiveness.J Virol. 2013 Nov;87(22):12327-38. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02132-13. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24027304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaronson, D. S., and C. M. Horvath. 2002. A road map for those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science 296:1653-1655. - PubMed
-
- Basler, C. F., and A. Garcia-Sastre. 2002. Viruses and the type I interferon antiviral system: induction and evasion. Int. Rev. Immunol. 21:305-337. - PubMed
-
- Blondel, D., T. Regad, N. Poisson, B. Pavie, H. Harper, P. P. Pandolfi, H. De The, and M. K. Chelbi-Alix. 2002. Rabies virus P and small P products interact directly with PML and reorganize PML nuclear bodies. Oncogene 21:7957-7970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

