Analysis of biogenic amine variability among individual fly heads with micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography-electrochemical detection
- PMID: 16255588
- PMCID: PMC1362073
- DOI: 10.1021/ac050963m
Analysis of biogenic amine variability among individual fly heads with micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography-electrochemical detection
Abstract
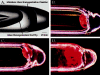
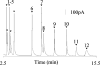
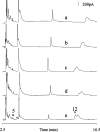
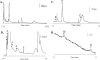
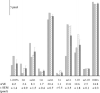
Neurochemical variability among individual Drosophila heads has been examined with the sensitivity of electrochemical detection and the selectivity of micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. Homogenization of single Drosophila heads in volumes as small as 100 nL has been accomplished. Here we demonstrate reproducible separations for single fly heads in 250-nL volumes providing a 4-fold increase in sensitivity without overloading the electrochemical detector. This increase in sensitivity allows detection of previously undetected analytes, such as N-acetyltyramine (naTA) and octopamine (OA). Analytes including L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, N-acetyl octopamine, N-acetyldopamine, naTA, N-acetylserotonin, OA, dopamine, tyramine, and serotonin also have been consistently identified in single-head homogenates and observed with homogenates representing populations of Drosophila. Neurochemical variation between individual flies as well as the consistency within a population indicates varying amounts of neurotransmitter turnover. The inception, design, and fabrication of a miniature tissue homogenizer has enabled the separation of biogenic amines and metabolites from these severely volume-limited single Drosophila head homogenates.
Figures
References
-
- Brown AS, Gershon S. J. Neural Transm. Gen. Sect. 1993;91:75–109. - PubMed
-
- Miyamoto S, Duncan GE, Marx CE, Lieberman JA. Mol. Psychiatry. 2005;10:79–104. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa N. Neurology. 1998;51:S13–20. - PubMed
-
- Stoof JC, Winogrodzka A, van Muiswinkel FL, Wolters EC, Voorn P, Groenewegen HJ, Booij J, Drukarch B. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999;375:75–86. - PubMed
-
- Powell PR, Ewing AG. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005;382:581–591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

