5-HT1B receptors modulate the feeding inhibitory effects of enterostatin
- PMID: 16256085
- PMCID: PMC2526559
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.09.029
5-HT1B receptors modulate the feeding inhibitory effects of enterostatin
Abstract
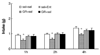
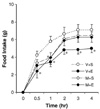
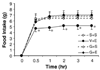
Serotonin (5-HT) is considered to play an important role in control of appetite. Enterostatin has been shown to alter 5-HT release in the brain, and non-specific 5-HT antagonists blocked the anorectic response to icv enterostatin. The aim of this study was to further identify which 5-HT receptor subtype mediates the enterostatin feeding behavior and whether this effect occurs due to action in the PVN. Wild-type and 5-HT2C receptor-/- (KO) mice and normal Sprague-Dawley rats were used in these experiments. All animals were fed a high fat diet. Enterostatin (120 nmol, i.p.) reduced the intake of high fat diet in 5-HT2C receptor mutant mice (saline 4.54 +/- 0.47 kcal vs. Ent 2.53 +/- 0.76 kcal) 1 h after injection. A selective 5-HT1B antagonist (GR55526, 40 mg/kg body weight, i.p.) blocked the enterostatin hypophagic effects in these KO mice. Rats were implanted with cannulas into the amygdala and the ipsilateral PVN. The 5-HT receptor antagonists metergoline (non-specific receptor subtypes 1 and 2), or ritanserin (selective 2C), or GR55562 (selective l B) was injected into the PVN prior to enterostatin (0.01 nmol) injection into the amygdala. Enterostatin reduced food intake (saline: 5.80 +/- 0.59 g vs. enterostatin 3.47 +/- 0.56 g, P < 0.05 at l h). Pretreatment with either metergoline (10 nmol) or GR55526 (10 nmol) but not ritanserin (10 nmol) into the PVN attenuated the anorectic response to amygdala enterostatin. The data imply that the enterostatin anorectic response may be modulated by 5-HT1B receptors and that a neuronal pathway from the amygdala to the PVN regulates the enterostatin response through activation of 5-HTlB receptors in PVN.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enterostatin actions in the amygdala and PVN to suppress feeding in the rat.Peptides. 1997;18(9):1341-7. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(97)00191-5. Peptides. 1997. PMID: 9392835
-
Amygdala enterostatin induces c-Fos expression in regions of hypothalamus that innervate the PVN.Brain Res. 2004 Sep 10;1020(1-2):147-53. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.06.029. Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15312796
-
Changes in the microstructure of feeding after administration of enterostatin into the paraventricular nucleus and the amygdala.Peptides. 1998;19(3):557-62. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(97)00460-9. Peptides. 1998. PMID: 9533645
-
Enterostatin--a peptide regulating fat intake.Obes Res. 1997 Jul;5(4):360-72. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1997.tb00565.x. Obes Res. 1997. PMID: 9285845 Review.
-
Enterostatin and its target mechanisms during regulation of fat intake.Physiol Behav. 2004 Dec 30;83(4):623-30. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.08.040. Physiol Behav. 2004. PMID: 15621068 Review.
Cited by
-
[18F]FDG-PET and [18F]MPPF-PET are brain biomarkers for the creatine transporter Slc6a8 loss of function mutation.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 1;15(1):7280. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92022-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40025148 Free PMC article.
-
Different metabolic responses to central and peripheral injection of enterostatin.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006 Apr;290(4):R909-15. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00045.2005. Epub 2005 Dec 8. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16339388 Free PMC article.
-
Enterostatin inhibition of dietary fat intake is modulated through the melanocortin system.Peptides. 2007 Mar;28(3):643-9. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2006.10.003. Epub 2006 Nov 17. Peptides. 2007. PMID: 17113194 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic control of feeding microstructure in Drosophila.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Jan 17;16:1105579. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1105579. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36733453 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal regulation of food intake.J Clin Invest. 2007 Jan;117(1):13-23. doi: 10.1172/JCI30227. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17200702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alheid GF, de Olmos JS, Beltramino CA. Amygdala and extended amygdala. In: Paxinos G, editor. The Rat Nervous System. London: Academic; 1995. pp. 495–500.
-
- Blundell JE. Is there a role for serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) in feeding? Int. J. Obes. 1977;1:15–42. - PubMed
-
- Blundell JE, Halford JC. Serotonin and appetite regulation. CNS Drugs. 1998;6:473–495.
-
- Bruinvels AT, Landwehrmeyer B, Gustafson EL, Durkin MM, Mengod G, Branchek TA, Hoyer D, Palacios JM. Localization of 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D alpha, 5-HT1E and 5-HT1F receptor messenger RNA in rodent and primate brain. Neuropharmacology. 1994;33:367–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

