A method to find tissue-specific novel sites of selective adenosine deamination
- PMID: 16257978
- PMCID: PMC1275595
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gni169
A method to find tissue-specific novel sites of selective adenosine deamination
Abstract
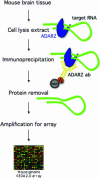
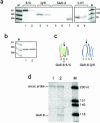
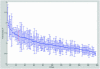
Site-selective adenosine (A) to inosine (I) RNA editing by the ADAR enzymes has been found in a variety of metazoan from fly to human. Here we describe a method to detect novel site-selective A to I editing that can be used on various tissues as well as species. We have shown previously that there is a preference for ADAR2-binding to selectively edited sites over non-specific interactions with random sequences of double-stranded RNA. The method utilizes immunoprecipitation (IP) of intrinsic RNA-protein complexes to extract substrates subjected to site-selective editing in vivo, in combination with microarray analyses of the captured RNAs. We show that known single sites of A to I editing can be detected after IP using an antibody against the ADAR2 protein. The RNA substrates were verified by RT-PCR, RNase protection and microarray. Using this method it is possible to uniquely identify novel single sites of selective A to I editing.
Figures
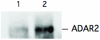
References
-
- Levanon E.Y., Eisenberg E., Yelin R., Nemzer S., Hallegger M., Shemesh R., Fligelman Z.Y., Shoshan A., Pollock S.R., Sztybel D., et al. Systematic identification of abundant A-to-I editing sites in the human transcriptome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004;22:1001–1005. - PubMed

