The structure of polyunsaturated lipid bilayers important for rhodopsin function: a neutron diffraction study
- PMID: 16258049
- PMCID: PMC1367042
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.071712
The structure of polyunsaturated lipid bilayers important for rhodopsin function: a neutron diffraction study
Abstract
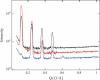
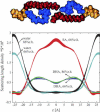
The structure of oriented 1-stearoyl-2-docosahexaenoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine bilayers with perdeuterated stearoyl- or docosahexaenoyl hydrocarbon chains was investigated by neutron diffraction. Experiments were conducted at two different relative humidities, 66 and 86%. At both humidities we observed that the polyunsaturated docosahexaenoyl chain has a preference to reside near the lipid water interface. That leaves voids in the bilayer center that are occupied by saturated stearoyl chain segments. This uneven distribution of saturated- and polyunsaturated chain densities is likely to result in membrane elastic stress that modulates function of integral receptor proteins like rhodopsin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure and dynamics of cholesterol-containing polyunsaturated lipid membranes studied by neutron diffraction and NMR.J Membr Biol. 2011 Jan;239(1-2):63-71. doi: 10.1007/s00232-010-9326-6. Epub 2010 Dec 14. J Membr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21161517 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of docosahexaenoic acid-containing phospholipid bilayers as studied by (2)H NMR and molecular dynamics simulations.J Am Chem Soc. 2002 Jan 16;124(2):298-309. doi: 10.1021/ja011383j. J Am Chem Soc. 2002. PMID: 11782182
-
Polyunsaturated docosahexaenoic vs docosapentaenoic acid-differences in lipid matrix properties from the loss of one double bond.J Am Chem Soc. 2003 May 28;125(21):6409-21. doi: 10.1021/ja029029o. J Am Chem Soc. 2003. PMID: 12785780
-
Structure and dynamics of polyunsaturated hydrocarbon chains in lipid bilayers-significance for GPCR function.Chem Phys Lipids. 2008 May;153(1):64-75. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2008.02.016. Epub 2008 Mar 13. Chem Phys Lipids. 2008. PMID: 18396152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of X-Ray and Neutron Scattering Methods with Volume Measurements to Determine Lipid Bilayer Structure and Number of Water Molecules/Lipid.Subcell Biochem. 2015;71:17-43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-19060-0_2. Subcell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26438260 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydration of POPC bilayers studied by 1H-PFG-MAS-NOESY and neutron diffraction.Eur Biophys J. 2007 Apr;36(4-5):281-91. doi: 10.1007/s00249-007-0142-6. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Eur Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17333162 Free PMC article.
-
Association of lipidome remodeling in the adipocyte membrane with acquired obesity in humans.PLoS Biol. 2011 Jun;9(6):e1000623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000623. Epub 2011 Jun 7. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21666801 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical and biochemical mechanisms by which dietary N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids from fish oil disrupt membrane lipid rafts.J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Feb;23(2):101-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Nutr Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22137258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brominated lipid probes expose structural asymmetries in constricted membranes.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023 Feb;30(2):167-175. doi: 10.1038/s41594-022-00898-1. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36624348 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids do not fluidify bilayers in the liquid-crystalline state.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 2;8(1):16240. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34264-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30389959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salem, N., B. Litman, H. Y. Kim, and K. Gawrisch. 2001. Mechanisms of action of docosahexaenoic acid in the nervous system. Lipids. 36:945–959. - PubMed
-
- Worcester, D. L., and N. P. Franks. 1976. Structural analysis of hydrated egg lecithin and cholesterol bilayers. II. Neutron diffraction. J. Mol. Biol. 100:359–378. - PubMed
-
- Bacon, G. E., and R. D. Lowde. 1948. Secondary extinction and neutron crystallography. Acta. Crystallogr. 1:303–314.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

