Platelets mediate cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced liver damage
- PMID: 16258538
- PMCID: PMC2908083
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1317
Platelets mediate cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced liver damage
Abstract
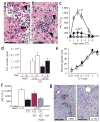
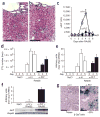
We found that platelet depletion reduces intrahepatic accumulation of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and organ damage in mouse models of acute viral hepatitis. Transfusion of normal but not activation-blocked platelets in platelet-depleted mice restored accumulation of CTLs and severity of disease. In contrast, anticoagulant treatment that prevented intrahepatic fibrin deposition without reducing platelet counts did not avert liver injury. Thus, activated platelets contribute to CTL-mediated liver immunopathology independently of procoagulant function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:65–91. - PubMed
-
- Wilson JM. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;46:205–209. - PubMed
-
- Weyrich AS, Lindemann S, Zimmerman GA. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:1897–1905. - PubMed
-
- Weyrich AS, Zimmerman GA. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Ando K, et al. J Immunol. 1994;152:3245–3253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 NS054193/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS052465/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA040489/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA40489/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL042846/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA040489/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL031950/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL42846/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI40696/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS054143/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL31950/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS061107/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL042846/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042893/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057711/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040696/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL078784/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL78784/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

