Specificity of receptor-ligand interactions and their effect on dimerisation as observed by electrospray mass spectrometry: bile acids form stable adducts to the RXRalpha
- PMID: 16258897
- PMCID: PMC2315782
- DOI: 10.1002/jms.925
Specificity of receptor-ligand interactions and their effect on dimerisation as observed by electrospray mass spectrometry: bile acids form stable adducts to the RXRalpha
Abstract
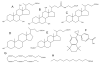
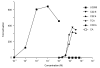
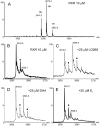
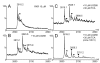
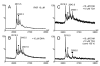
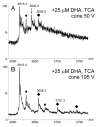
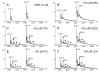
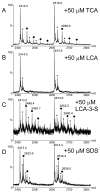
Electrospray (ES) mass spectrometry data is presented showing that agonist binding to the nuclear receptor (NR), retinoid X receptor alpha (RXRalpha), is competitive. The competitive nature of agonist binding can be used to discriminate between the specific and non-specific binding of small lipophilic molecules to NRs. Further, data is presented which show that high-affinity ligand binding to the RXRalpha ligand-binding domain (LBD) stabilises the domain homodimer. The results indicate that homodimerisation, a functional property of the receptor associated with the binding of agonist ligands, could be used to discriminate between specific and non-specific binding events. Additionally, we report on the remarkable stability of the gas-phase complex between the RXRalpha LBD protein and endogenous bile acids. Protein-bile acid interactions in the gas phase were found to be surprisingly strong, withstanding 'in-source' fragmentation in the ES interface, and, in the case of taurocholic acid (TCA) and lithocholic acid-3-sulphate (LCA-3-sulphate), collision-induced dissociation within the collision cell of a tandem mass spectrometer. Bile acids were found to be inactive towards RXRalpha in transfection assays, and have not been reported to be ligands for the RXRalpha, although lithocholic acid (LCA) has been found to be a competitor in the photoaffinity labelling of RXRbeta with 9-cis-retinoic acid (9-cis-RA). The observation of strong RXRalpha-bile acid non-covalent complexes in ES mass spectrometry highlight the danger of extrapolating gas-phase binding data to the solution phase and further to a possible biological activity, particularly when surface-active compounds such as bile acids are involved. The introduction of a competitive ligand-binding experiment can alleviate this problem and allow the differentiation between specific and non-specific binding.
Copyright 2005 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electrospray mass spectrometry for the direct accurate mass measurement of ligands in complex with the retinoid X receptor alpha ligand binding domain.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005 Oct;16(10):1631-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2005.06.003. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005. PMID: 16085421
-
Heterodimer formation with retinoic acid receptor RXRα modulates coactivator recruitment by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor PPARγ.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jul;297(1):100814. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100814. Epub 2021 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34081964 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of two residues converts the ligand-binding domain of RXRα into a uniform monomer without impairing the binding of retinoic acid and cofactors.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Jan 29;642:50-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.12.042. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 36563628
-
Dimerization of nuclear receptors.Methods Cell Biol. 2013;117:21-41. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-408143-7.00002-5. Methods Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24143970 Review.
-
Overview of the structure-based non-genomic effects of the nuclear receptor RXRα.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018 Aug 7;23:36. doi: 10.1186/s11658-018-0103-3. eCollection 2018. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30093910 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Directed evolution of Vibrio fischeri LuxR for improved response to butanoyl-homoserine lactone.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Sep;73(18):5775-81. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00060-07. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17675429 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for ligands of human retinoid X receptor-alpha using ultrafiltration mass spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2007 Dec 15;79(24):9398-402. doi: 10.1021/ac701701k. Epub 2007 Nov 13. Anal Chem. 2007. PMID: 17997524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giguère V. Orphan nuclear receptors: from gene to function. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:689. - PubMed
-
- Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995;83:841. - PubMed
-
- Steinmetz AC, Renaud JP, Moras D. Binding of ligands and activation of transcription by nuclear receptors. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2001;30:329. - PubMed
-
- Chawla A, Repa JJ, Evans RM, Mangelsdorf DJ. Nuclear receptors and lipid physiology: opening the X-files. Science. 2001;294:1866. - PubMed
-
- Kallen JA, Schlaeppi JM, Bitsch F, Geisse S, Geiser M, Delhon I, Fournier B. X-Ray Structure of the hRORalpha LBD at 1.63 A. Structural and Functional Data that Cholesterol or a Cholesterol Derivative Is the Natural Ligand of RORalpha. Structure (Camb) 2002;10:1697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

