Genetic control of thymic development of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T lymphocytes
- PMID: 16259008
- PMCID: PMC2755768
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200535225
Genetic control of thymic development of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T lymphocytes
Abstract
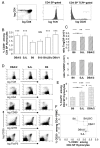
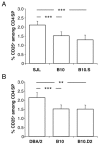
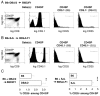
Among the several mechanisms known to be involved in the establishment and maintenance of immunological tolerance, the activity of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T lymphocytes has recently incited most interest because of its critical role in inhibition of autoimmunity and anti-tumor immunity. Surprisingly, very little is known about potential genetic modulation of intrathymic regulatory T lymphocyte development. We show that distinct proportions of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells are found in thymi of common laboratory mouse strains. We demonstrate that distinct levels of phenotypically identical regulatory T cells develop with similar kinetics in the mice studied. Our experimental data on congenic mouse strains indicate that differences are not caused by the distinct MHC haplotypes of the inbred mouse strains. Moreover, the responsible loci act in a thymocyte-intrinsic manner, confirming the latter conclusion. We have not found any correlation between thymic and peripheral levels of regulatory T cells, consistent with known homeostatic expansion and/or retraction of the peripheral regulatory T cell pool. Our data indicate that polymorphic genes modulate differentiation of regulatory T cells. Identification of responsible genes may reveal novel clinical targets and still elusive regulatory T cell-specific markers. Importantly, these genes may also modulate susceptibility to autoimmune disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An MHC-linked locus modulates thymic differentiation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T lymphocytes.Int Immunol. 2006 Nov;18(11):1509-19. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxl084. Epub 2006 Aug 30. Int Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16943258 Free PMC article.
-
Agonist ligands expressed by thymic epithelium enhance positive selection of regulatory T lymphocytes from precursors with a normally diverse TCR repertoire.J Immunol. 2006 Jul 15;177(2):1101-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.1101. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16818767 Free PMC article.
-
Thymus and autoimmunity: production of CD25+CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells as a key function of the thymus in maintaining immunologic self-tolerance.J Immunol. 1999 May 1;162(9):5317-26. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10228007
-
Human regulatory T cells: a unique, stable thymic subset or a reversible peripheral state of differentiation?Immunol Lett. 2007 Nov 30;114(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.08.012. Epub 2007 Sep 29. Immunol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17945352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of thymically derived natural regulatory T cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jan;1183:1-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05129.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20146704 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory T cells in the face of the intestinal microbiota.Nat Rev Immunol. 2023 Nov;23(11):749-762. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00890-w. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37316560 Review.
-
Unstable FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in NZW mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 2;113(5):1345-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1524660113. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26768846 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerance induction or sensitization in mice exposed to noninherited maternal antigens (NIMA).Am J Transplant. 2008 Nov;8(11):2307-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02417.x. Am J Transplant. 2008. PMID: 18925902 Free PMC article.
-
Increased T regulatory cells lead to development of Th2 immune response in male SJL mice.Autoimmunity. 2011 May;44(3):219-28. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2010.519746. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Autoimmunity. 2011. PMID: 20883149 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of regulatory T cells in the thymus.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012 Feb 10;12(3):157-67. doi: 10.1038/nri3155. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22322317 Review.
References
-
- Stockinger B. T lymphocyte tolerance: from thymic deletion to peripheral control mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1999;71:229–265. - PubMed
-
- Waldmann H, Graca L, Cobbold S, Adams E, Tone M, Tone Y. Regulatory T cells and organ transplantation. Semin Immunol. 2004;16:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:531–562. - PubMed
-
- Piccirillo CA, Shevach EM. Naturally-occurring CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells: central players in the arena of peripheral tolerance. Semin Immunol. 2004;16:81–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

