Nicotine enhances both foreground and background contextual fear conditioning
- PMID: 16260086
- PMCID: PMC2697563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.10.026
Nicotine enhances both foreground and background contextual fear conditioning
Abstract
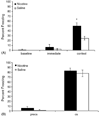
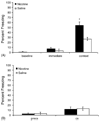
The present study examined if nicotine enhances contextual fear conditioning when the training context is either a background stimulus or a foreground stimulus. In the background conditioning experiment, mice were trained using two auditory conditioned stimulus (CS; 30 s, 85 dB white noise)-footshock unconditioned stimulus (US; 2 s, 0.57 mA) pairings and tested 24 h later. In the foreground conditioning experiment, mice were trained with two presentations of a footshock US (2 s, 0.57 mA) and tested 24 h later. Mice received 0.09 mg/kg nicotine before training and testing. For both the foreground and background conditioning experiments, nicotine enhanced contextual conditioning. No enhancement of the auditory CS-US association was seen. These results demonstrate that nicotine enhances contextual fear conditioning regardless of whether the context is a background stimulus or a foreground stimulus during conditioning.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nicotine produces a within-subject enhancement of contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice independent of sex.Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 2003 Apr-Jun;38(2):124-32. doi: 10.1007/BF02688830. Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 2003. PMID: 14527181
-
beta2 subunit-containing nicotinic receptors mediate the enhancing effect of nicotine on trace cued fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007 Feb;190(3):343-52. doi: 10.1007/s00213-006-0624-8. Epub 2006 Nov 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17136517 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine enhances trace cued fear conditioning but not delay cued fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice.Behav Brain Res. 2004 Nov 5;155(1):167-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2004.04.009. Behav Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15325790
-
Nicotine enhancement of contextual fear conditioning.Behav Brain Res. 1999 Jul;102(1-2):31-9. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(98)00157-0. Behav Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10403013
-
Acute nicotine delays extinction of contextual fear in mice.Behav Brain Res. 2014 Apr 15;263:133-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.01.031. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Behav Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24487010 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of drugs of abuse on hippocampal plasticity and hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: contributions to development and maintenance of addiction.Learn Mem. 2016 Sep 15;23(10):515-33. doi: 10.1101/lm.042192.116. Print 2016 Oct. Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27634143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inbred mouse strain differences in alcohol and nicotine addiction-related phenotypes from adolescence to adulthood.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022 Jul;218:173429. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2022.173429. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022. PMID: 35820468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotine modulates contextual fear extinction through changes in ventral hippocampal GABAergic function.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Oct;141:192-200. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.08.019. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 30170085 Free PMC article.
-
Acute nicotine treatment enhances compulsive-like remifentanil self-administration that persists despite contextual punishment.Addict Biol. 2022 May;27(3):e13170. doi: 10.1111/adb.13170. Addict Biol. 2022. PMID: 35470562 Free PMC article.
-
Contingency management and cognitive behavioral therapy for trauma-exposed smokers with and without posttraumatic stress disorder.Addict Behav. 2019 Mar;90:136-142. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.10.042. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Addict Behav. 2019. PMID: 30391774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC. Passive and active reactions to fear-eliciting stimuli. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1969;68:129–135. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Fial RA. Effects of limbic lesions on passive avoidance and reactivity to shock. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1968;66:606–612. - PubMed
-
- Crusio WE, Schwegler H, van Abeelen JH. Behavioral responses to novelty and structural variation of the hippocampus in mice. II. Multivariate genetic analysis. Behav., Brain Res. 1989;32:81–88. - PubMed
-
- Davis JA, Gould TJ. The effects of DHBE and MLA on nicotine induced enhancement of contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice. Psychopharmacology. in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

