Some environmental contaminants influence motor and feeding behaviors in the ornate wrasse (Thalassoma pavo) via distinct cerebral histamine receptor subtypes
- PMID: 16263506
- PMCID: PMC1310913
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.7983
Some environmental contaminants influence motor and feeding behaviors in the ornate wrasse (Thalassoma pavo) via distinct cerebral histamine receptor subtypes
Erratum in
- Environ Health Perspect. 2005 Dec;113(12):A807
Abstract
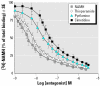
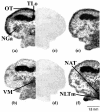
Common environmental contaminants such as heavy metals and pesticides pose serious risks to behavioral and neuroendocrine functions of many aquatic organisms. In the present study, we show that the heavy metal cadmium and the pesticide endosulfan produce such effects through an interaction of specific cerebral histamine receptor subtypes in the teleost ornate wrasse (Thalassoma pavo). Treatment of this teleost with toxic cadmium levels for 1 week was sufficient to induce abnormal swimming movements, whereas reduced feeding behaviors were provoked predominantly by elevated endosulfan concentrations. In the brain, these environmental contaminants caused neuronal degeneration in cerebral targets such as the mesencephalon and hypothalamus, damage that appeared to correlate with altered binding levels of the three major histamine receptors (subtypes 1, 2, and 3). Although cadmium accounted for reduced binding activity of all three subtypes in most brain regions, it was subtype 2 that seemed to be its main target, as shown by a very great (p < 0.001) down-regulation in mesencephalic areas such as the stratum griseum central layer. Conversely, endosulfan provided very great and great (p < 0.01) up-regulating effects of subtype 3 and 1 levels, respectively, in preoptic-hypothalamic areas such as the medial part of the lateral tuberal nucleus, and in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. These results suggest that the neurotoxicant-dependent abnormal motor and feeding behaviors may well be tightly linked to binding activities of distinct histamine subtypes in localized brain regions of the Thalassoma pavo.
Figures



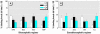
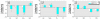

Similar articles
-
Light- and dark-dependent orexinergic neuronal signals promote neurodegenerative phenomena accounting for distinct behavioral responses in the teleost Thalassoma pavo.J Neurosci Res. 2009 Feb 15;87(3):748-57. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21886. J Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 18816789
-
Orexin-A Rescues Chronic Copper-Dependent Behavioral and HSP90 Transcriptional Alterations in the Ornate Wrasse Brain.Neurotox Res. 2017 May;31(4):578-589. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9706-0. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 28188453
-
ORX neuroreceptor system and HSP90 are linked to recovery strategies against copper toxicity in Thalassoma pavo.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Jan;137(1):135-46. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft229. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24122842
-
Environmental stressors and neurobiological features of marine teleosts: histamine receptors as targets.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2010 Aug;40(7):620-32. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2010.487479. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20569195 Review.
-
Histamine in brain development and tumors.Semin Cancer Biol. 2000 Feb;10(1):11-4. doi: 10.1006/scbi.2000.0302. Semin Cancer Biol. 2000. PMID: 10888266 Review.
Cited by
-
Temperature and Estrogen Alter Predator-Prey Interactions between Fish Species.Integr Org Biol. 2020 Apr 1;2(1):obaa008. doi: 10.1093/iob/obaa008. eCollection 2020. Integr Org Biol. 2020. PMID: 33791552 Free PMC article.
-
Using sets of behavioral biomarkers to assess short-term effects of pesticide: a study case with endosulfan on frog tadpoles.Ecotoxicology. 2012 May;21(4):1240-50. doi: 10.1007/s10646-012-0878-3. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Ecotoxicology. 2012. PMID: 22383141
References
-
- Airaksinen MS, Panula P. Comparative neuroanatomy of the hystaminergic system in the brain of the frog Xenopus laevis. J Comp Neurol. 1990;292:412–423. - PubMed
-
- Bass AH, Grober MS. Social and neural modulation of sexual plasticity in teleost fish. Brain Behav Evol. 2001;57:293–300. - PubMed
-
- Beauvais SL, Jones SB, Parris JT, Brewer SK, Little EE. Cholinergic and behavioral neurotoxicity of carbaryl and cadmium to larval rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2001;49:84–90. - PubMed
-
- Bellas J, Vasquez E, Beiras R. Toxicity of Hg, Cu and Cr on early developmental stages of Ciona intestinalis (Chordata, Ascidiacea) with potential application marine water quality assessment. Water Res. 2001;35(12):2905–12. - PubMed
-
- Bisson M, Hontela A. Cytotoxic and endocrine-disrupting potential of atrazine, diazinon, endosulfan, and mancozeb in adrenocortical steroidogenic cells of rainbow trout exposed in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002;180:110–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

