The Drosophila nucleosome remodeling factor NURF is required for Ecdysteroid signaling and metamorphosis
- PMID: 16264191
- PMCID: PMC1276728
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1342605
The Drosophila nucleosome remodeling factor NURF is required for Ecdysteroid signaling and metamorphosis
Abstract
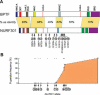
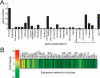
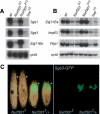
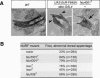
Drosophila NURF is an ISWI-containing ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex that regulates transcription by catalyzing nucleosome sliding. To determine in vivo gene targets of NURF, we performed whole genome expression analysis on mutants lacking the NURF-specific subunit NURF301. Strikingly, a large set of ecdysone-responsive targets is included among several hundred NURF-regulated genes. Null Nurf301 mutants do not undergo larval to pupal metamorphosis, and also enhance dominant-negative mutations in ecdysone receptor. Moreover, purified NURF binds EcR in an ecdysone-dependent manner, suggesting it is a direct effector of nuclear receptor activity. The conservation of NURF in mammals has broad implications for steroid signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Andres A.J. and Cherbas, P. 1992. Tissue-specific ecdysone responses: Regulation of the Drosophila genes Eip28/29 and Eip40 during larval development. Development 116: 865-876. - PubMed
-
- Andres A.J. and Thummel, C.S. 1995. The Drosophila 63F early puff contains E63-1, an ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes a novel Ca2+-binding protein. Development 121: 2667-2679. - PubMed
-
- Andres A.J., Fletcher, J.C., Karim, F.D., and Thummel, C.S. 1993. Molecular analysis of the initiation of insect metamorphosis: A comparative study of Drosophila ecdysteroid-regulated transcription. Dev. Biol. 160: 388-404. - PubMed
-
- Arbeitman M.N., Furlong, E.E., Imam, F., Johnson, E., Null, B.H., Baker, B.S., Krasnow, M.A., Scott, M.P., Davis, R.W., and White, K.P. 2002. Gene expression during the life cycle of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 297: 2270-2275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
