CAR-1, a protein that localizes with the mRNA decapping component DCAP-1, is required for cytokinesis and ER organization in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos
- PMID: 16267265
- PMCID: PMC1345671
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-09-0874
CAR-1, a protein that localizes with the mRNA decapping component DCAP-1, is required for cytokinesis and ER organization in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos
Abstract
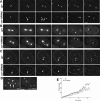
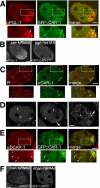
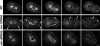
The division of one cell into two requires the coordination of multiple components. We describe a gene, car-1, whose product may provide a link between disparate cellular processes. Inhibition of car-1 expression in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos causes late cytokinesis failures: cleavage furrows ingress but subsequently regress and the spindle midzone fails to form, even though midzone components are present. The localized accumulation of membrane that normally develops at the apex of the cleavage furrow during the final phase of cytokinesis does not occur and organization of the endoplasmic reticulum is aberrant, indicative of a disruption in membrane trafficking. The car-1 gene has homologues in a number of species, including proteins that associate with RNA binding proteins. CAR-1 localizes to P-granules (germ-line specific ribonucleoprotein particles) and discrete, developmentally regulated cytoplasmic foci. These foci also contain DCAP-1, a protein involved in decapping mRNAs. Thus, CAR-1, a protein likely to be associated with RNA metabolism, plays an essential role in the late stage of cytokinesis, suggesting a novel link between RNA, membrane trafficking and cytokinesis in the C. elegans embryo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Condensin and the spindle midzone prevent cytokinesis failure induced by chromatin bridges in C. elegans embryos.Curr Biol. 2013 Jun 3;23(11):937-46. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.04.028. Epub 2013 May 16. Curr Biol. 2013. PMID: 23684975 Free PMC article.
-
A complex containing the Sm protein CAR-1 and the RNA helicase CGH-1 is required for embryonic cytokinesis in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Cell Biol. 2005 Oct 24;171(2):267-79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200506124. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16247027 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing the effects of delaying aster separation on furrow formation during cytokinesis in the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Jan 1;21(1):50-62. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-01-0089. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 19889842 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokinesis in the C. elegans embryo: regulating contractile forces and a late role for the central spindle.Cell Struct Funct. 2001 Dec;26(6):603-7. doi: 10.1247/csf.26.603. Cell Struct Funct. 2001. PMID: 11942615 Review.
-
The P Granules of C. elegans: A Genetic Model for the Study of RNA-Protein Condensates.J Mol Biol. 2018 Nov 2;430(23):4702-4710. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.08.007. Epub 2018 Aug 8. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30096346 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamin participates in the maintenance of anterior polarity in the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo.Dev Cell. 2009 Jun;16(6):889-900. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.04.009. Dev Cell. 2009. PMID: 19531359 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic mechanisms promote cell-type-specific cytokinetic diversity.Elife. 2018 Jul 20;7:e36204. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36204. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30028292 Free PMC article.
-
RNA granules in germ cells.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Dec 1;3(12):a002774. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002774. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21768607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P granule assembly and function in Caenorhabditis elegans germ cells.J Androl. 2010 Jan-Feb;31(1):53-60. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.109.008292. Epub 2009 Oct 29. J Androl. 2010. PMID: 19875490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profiling of the mammalian mitotic spindle proteome reveals an ER protein, OSTD-1, as being necessary for cell division and ER morphology.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 10;8(10):e77051. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077051. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24130834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht, M., and Lengauer, T. (2004). Novel Sm-like proteins with long C-terminal tails and associated methyltransferases. FEBS Lett. 569, 18-26. - PubMed
-
- Badrinath, A. S., and White, J. G. (2003). Contrasting patterns of mitochondrial redistribution in the early lineages of Caenorhabditis elegans and Acrobeloides sp. PS1146. Dev. Biol. 258, 70-75. - PubMed
-
- Blower, M. D., Nachury, M., Heald, R., and Weis, K. (2005). A Rae1-containing ribonucleoprotein complex is required for mitotic spindle assembly. Cell 121, 223-234. - PubMed
-
- Boag, P., Nakamura, A., and Blackwell, T. K. (2005). A conserved RNA-protein complex component involved in physiological germline apoptosis regulation in C. elegans. Development 132, 4975-4986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

