Exhaled nitric oxide: sources of error in offline measurement
- PMID: 16268114
- PMCID: PMC1866170
- DOI: 10.3200/AEOH.59.8.385-391
Exhaled nitric oxide: sources of error in offline measurement
Abstract
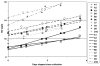
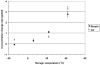
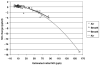
Delayed offline measurement of exhaled nitric oxide (eNO), although useful in environmental and clinical research, is limited by the instability of stored breath samples. The authors characterized sources of instability with the goal of minimizing them. Breath and other air samples were stored under various conditions, and NO levels were measured repeatedly over 1-7 d. Concentration change rates varied positively with temperature and negatively with initial NO level, thus "stable" levels reflected a balance of NO-adding and NO-removing processes. Storage under refrigeration for a standardized period of time can optimize offline eNO measurement, although samples at room temperature are effectively stable for several hours.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationships of online exhaled, offline exhaled, and ambient nitric oxide in an epidemiologic survey of schoolchildren.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2009 Nov;19(7):674-81. doi: 10.1038/jes.2008.64. Epub 2008 Oct 22. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 18941479
-
ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005 Apr 15;171(8):912-30. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200406-710ST. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. PMID: 15817806 No abstract available.
-
Exhaled nitric oxide in mylar balloons: influence of storage time, humidity and temperature.Mediators Inflamm. 2003 Feb;12(1):47-9. doi: 10.1080/0962935031000096971. Mediators Inflamm. 2003. PMID: 12745548 Free PMC article.
-
Markers of lung disease in exhaled breath: nitric oxide.Biol Res Nurs. 2006 Apr;7(4):241-55. doi: 10.1177/1099800405286131. Biol Res Nurs. 2006. PMID: 16581895 Review.
-
Exhaled nitric oxide: a novel biomarker of adverse respiratory health effects in epidemiological studies.Arch Environ Health. 2000 Nov-Dec;55(6):418-23. doi: 10.1080/00039890009604040. Arch Environ Health. 2000. PMID: 11128880 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA methylation in the arginase-nitric oxide synthase pathway is associated with exhaled nitric oxide in children with asthma.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Jul 15;184(2):191-7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201012-2029OC. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21512169 Free PMC article.
-
Exhaled nitric oxide, susceptibility and new-onset asthma in the Children's Health Study.Eur Respir J. 2011 Mar;37(3):523-31. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00021210. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Eur Respir J. 2011. PMID: 20634264 Free PMC article.
-
Storage conditions for stability of offline measurement of fractional exhaled nitric oxide after collection for epidemiologic research.BMC Pulm Med. 2012 Nov 2;12:68. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-12-68. BMC Pulm Med. 2012. PMID: 23116255 Free PMC article.
-
Ethane and n-pentane in exhaled breath are biomarkers of exposure not effect.Biomarkers. 2009 Feb;14(1):17-25. doi: 10.1080/13547500902730680. Biomarkers. 2009. PMID: 19283520 Free PMC article.
-
Exhaled nitric oxide in a population-based study of southern California schoolchildren.Respir Res. 2009 Apr 21;10(1):28. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-28. Respir Res. 2009. PMID: 19379527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Amsterdam JG, Nierkens S, Vos SG, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide: a novel biomarker of adverse respiratory health effects in epidemiological studies. Arch Environ Health. 2000;55:418–23. - PubMed
-
- Kharitonov SA, Barnes PJ. Clinical aspects of exhaled nitric oxide. Eur Respir J. 2000;16:781–92. - PubMed
-
- Kharitonov SA, Barnes PJ. State of the art: exhaled markers of pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1693–722. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society. Recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide in adults and children—1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:2104–17. - PubMed
-
- Baraldi E, de Jongste JC. Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide in children, 2001. Eur Respir J. 2002;20:223–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
