Parkinson's disease-associated mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 augment kinase activity
- PMID: 16269541
- PMCID: PMC1283829
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507360102
Parkinson's disease-associated mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 augment kinase activity
Abstract
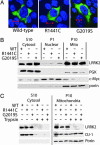
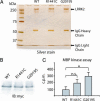
Mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 gene (LRRK2) cause late-onset Parkinson's disease (PD) with a clinical appearance indistinguishable from idiopathic PD. Initial studies suggest that LRRK2 mutations are the most common yet identified determinant of PD susceptibility, transmitted in an autosomal-dominant mode of inheritance. Herein, we characterize the LRRK2 gene and transcript in human brain and subclone the predominant ORF. Exogenously expressed LRRK2 protein migrates at approximately 280 kDa and is present largely in the cytoplasm but also associates with the mitochondrial outer membrane. Familial-linked mutations G2019S or R1441C do not have an obvious effect on protein steady-state levels, turnover, or localization. However, in vitro kinase assays using full-length recombinant LRRK2 reveal an increase in activity caused by familial-linked mutations in both autophosphorylation and the phosphorylation of a generic substrate. These results suggest a gain-of-function mechanism for LRRK2-linked disease with a central role for kinase activity in the development of PD.
Figures


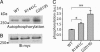

Comment in
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2: a new player with a familiar theme for Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Nov 15;102(46):16535-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508350102. Epub 2005 Nov 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16275903 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Funayama, M., Hasegawa, K., Kowa, H., Saito, M., Tsuji, S. & Obata, F. (2002) Ann. Neurol. 51, 296-301. - PubMed
-
- Zimprich, A., Biskup, S., Leitner, P., Lichtner, P., Farrer, M., Lincoln, S., Kachergus, J., Hulihan, M., Uitti, R. J., Calne, D. B., et al. (2004) Neuron 44, 601-607. - PubMed
-
- Paisan-Ruiz, C., Jain, S., Evans, E. W., Gilks, W. P., Simon, J., van der Brug, M., Lopez de Munain, A., Aparicio, S., Gil, A. M., Khan, N., et al. (2004) Neuron 44, 595-600. - PubMed
-
- Nichols, W. C., Pankratz, N., Hernandez, D., Paisan-Ruiz, C., Jain, S., Halter, C. A., Michaels, V. E., Reed, T., Rudolph, A., Shults, C. W., et al. (2005) Lancet 365, 410-412. - PubMed
-
- Di Fonzo, A., Rohe, C. F., Ferreira, J., Chien, H. F., Vacca, L., Stocchi, F., Guedes, L., Fabrizio, E., Manfredi, M., Vanacore, N., et al. (2005) Lancet 365, 412-415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

