Inhibitory effects of N-(4-hydrophenyl) retinamide on liver cancer and malignant melanoma cells
- PMID: 16270382
- PMCID: PMC4479673
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5763
Inhibitory effects of N-(4-hydrophenyl) retinamide on liver cancer and malignant melanoma cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of N-(4-hydrophenyl) retinamide (4-HPR), the derivative of retinoic acid, on inhibition of migration, invasion, cell growth, and induction of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HCCs) and malignant melanoma cells.
Methods: 4-HPR was chemically synthesized. Cellular migration and invasion were assayed by Borden chamber experiment. Cell growth was assayed by MTT chromometry. Apoptosis effect was measured using Hoechst 32258 staining and flow cytometry. Gene transfection was performed with lipofectamine.
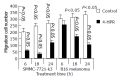
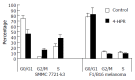
Results: We observed that the migration of HCC and melanoma cells was significantly suppressed by 4-HPR and the migration cells were reduced to 58+/-5.03 (control 201+/-27.2, P<0.05, n = 4) in SMMC 7721-k3 HCC, and to 254+/-25.04 (control 302+/-30.1, P<0.05, n = 4) in melanoma cells after 6-h incubation with 4-HPR. The invasion through reconstituted basement membrane was also significantly reduced by 4-HPR treatment to 11.2+/-3.3 in SMMC 7721-k3 HCC (control 27+/-13.1), and to 24.3+/-3.2 in melanoma cells (control 67.5+/-10.1, P<0.05, n = 3). Cell growth, especially in melanoma cells, was also significantly inhibited. Furthermore, 3 micromol/L of 4-HPR induced apoptosis in B16 melanoma cells (37.11+/-0.94%) more significantly than all-trans retinoic acid (P<0.05), but it failed to induce apoptosis in SMMC 7721-k3 HCC. The mechanism for 4-HPR-induced apoptosis was not clear, but we observed that 4-HPR could regulate p27(kip1), and overexpression of cerebroside sulfotransferase (CST) diminished the apoptosis induced by 4-HPR in melanoma cells.
Conclusion: 4-HPR is a potent inhibitor of HCC migration and inducer of melanoma cell apoptosis. CST and p27(kip1) expression might be associated with 4-HPR-induced apoptosis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Inhibitory effects on hepatocarcinoma and B16 melanoma cells by N-(4-hydrophenyl) retinamide].Shi Yan Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2003 Dec;36(6):421-7. Shi Yan Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 14724932 Chinese.
-
Is growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in lung cancer cell lines by fenretinide [N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide] sufficient for cancer therapy?Int J Cancer. 2002 Aug 10;100(5):520-6. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10525. Int J Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12124800
-
N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide is cytotoxic to melanoma cells in vitro through induction of programmed cell death.Int J Cancer. 1999 Apr 12;81(2):262-7. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19990412)81:2<262::aid-ijc16>3.0.co;2-a. Int J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10188729
-
Metabolism of N-[4-hydroxyphenyl]retinamide (4-HPR) to N-[4-methoxyphenyl]retinamide (4-MPR) may serve as a biomarker for its efficacy against human breast cancer and melanoma cells.Eur J Cancer. 1998 May;34(6):902-7. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(98)00032-x. Eur J Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9797705
-
Fenretinide in Cancer and Neurological Disease: A Two-Face Janus Molecule.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 4;23(13):7426. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137426. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806431 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory effects of retinoic acid on invasiveness of human thyroid carcinoma cell lines in vitro.J Endocrinol Invest. 2009 Oct;32(9):731-8. doi: 10.1007/BF03346528. J Endocrinol Invest. 2009. PMID: 19509478
-
Regulation of integrin αV subunit expression by sulfatide in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.J Lipid Res. 2013 Apr;54(4):936-52. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M031450. Epub 2013 Jan 22. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23345412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li X, Mikkelsen IM, Mortensen B, Winberg JO, Huseby NE. Butyrate reduces liver metastasis of rat colon carcinoma cells in vivo and resistance to oxidative stress in vitro. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2004;21:331–338. - PubMed
-
- Timmers M, Vekemans K, Vermijlen D, Asosingh K, Kuppen P, Bouwens L, Wisse E, Braet F. Interactions between rat colon carcinoma cells and Kupffer cells during the onset of hepatic metastasis. Int J Cancer. 2004;112:793–802. - PubMed
-
- Chuma M, Sakamoto M, Yasuda J, Fujii G, Nakanishi K, Tsuchiya A, Ohta T, Asaka M, Hirohashi S. Overexpression of cortactin is involved in motility and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2004;41:629–636. - PubMed
-
- Mann CD, Metcalfe MS, Leopardi LN, Maddern GJ. The clinical risk score: emerging as a reliable preoperative prognostic index in hepatectomy for colorectal metastases. Arch Surg. 2004;139:1168–1172. - PubMed
-
- Murakami T, Cardones AR, Hwang ST. Chemokine receptors and melanoma metastasis. J Dermatol Sci. 2004;36:71–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

