Association between thrombotic risk factors and extent of fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
- PMID: 16270394
- PMCID: PMC4479685
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5834
Association between thrombotic risk factors and extent of fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the prevalence of genetic and acquired prothrombotic risk factors and their association with the extent of fibrosis and fatty infiltration in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Methods: Forty-four patients with chronic hepatitis (28 men and 16 women, with mean age of 45+/-11 and 49+/-12 years, respectively) constituted the patient population of this study. The groups were divided as follows: 15 patients with fatty liver (FL); 15 with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH); 14 with chronic viral hepatitis (CH) diagnosed by histology and liver technetium scan or ultrasound; and 10 healthy individuals. Thrombophilic, coagulation factors and genetic mutations were diagnosed by standard hemostatic and molecular coagulation assays.
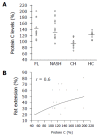
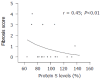
Results: Activated protein C (APC) resistance and protein S were the most prevalent thrombotic risk factors (6% and 10% in NAFLD vs 21% and 14% in CH; P<0.01 and P<0.05, respectively). One thrombotic risk factor was identified in 41% of patients (23% mild fibrosis, 18% severe fibrosis) and two thrombotic risk factors in 6% of patients with NAFLD and severe fibrosis. While no differences in APC ratio, lupus anticoagulant, fibrinogen, factor V Leiden, prothrombin, and MTHFR mutation were found. Protein S levels were significantly lower in NASH patients than in patients with FL alone (92+/-19 vs 106+/-2, P<0.01). Protein C levels were markedly higher in patients with NAFLD and mild or severe fibrosis as compared to the patients with CH, respectively (128+/-40 vs 96+/-14, P<0.001 or 129+/-36 vs 88+/-13, P<0.01).
Conclusion: Up to 46% of patients with NAFLD may have thrombotic risk factors, and the presence of thrombotic risk factors is correlated with the extent of hepatic fibrosis, suggesting a crucial role of the coagulation system in the pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis.
Figures
References
-
- Willner IR, Waters B, Patil SR, Reuben A, Morelli J, Riely CA. Ninety patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: insulin resistance, familial tendency, and severity of disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:2957–2961. - PubMed
-
- Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, Marchesini G, Brunello F, Carucci P, Musso A, De Paolis P, Capussotti L, Salizzoni M, et al. Expanding the natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1221–1231. - PubMed
-
- Assy N, Kaita K, Mymin D, Levy C, Rosser B, Minuk G. Fatty infiltration of liver in hyperlipidemic patients. Dig Dis Sci. 2000;45:1929–1934. - PubMed
-
- Bellentani S, Saccoccio G, Masutti F, Crocè LS, Brandi G, Sasso F, Cristanini G, Tiribelli C. Prevalence of and risk factors for hepatic steatosis in Northern Italy. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132:112–117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical