EGO-1, a putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, is required for heterochromatin assembly on unpaired dna during C. elegans meiosis
- PMID: 16271877
- PMCID: PMC4098869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.09.049
EGO-1, a putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, is required for heterochromatin assembly on unpaired dna during C. elegans meiosis
Abstract
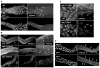
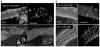
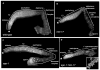
During meiosis in C. elegans, unpaired chromosomes and chromosomal regions accumulate high levels of histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2), a modification associated with facultative heterochromatin assembly and the resulting transcriptional silencing. Meiotic silencing of unpaired DNA may be a widely conserved genome defense mechanism. The mechanisms of meiotic silencing remain unclear, although both transcriptional and posttranscriptional processes are implicated. Cellular RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRPs) function in development and RNA-mediated silencing in many species and in heterochromatin assembly in S. pombe. There are four C. elegans RdRPs, including two with known germline functions. EGO-1 is required for fertility and robust germline RNAi. RRF-3 acts genetically to repress RNAi and is required for normal meiosis and spermatogenesis at elevated temperatures (S. L'Hernault, personal communication). Among C. elegans RdRPs, we find that only EGO-1 is required for H3K9me2 enrichment on unpaired chromosomal regions during meiosis. This H3K9me2 enrichment does not require Dicer or Drosha nuclease or any of several other proteins required for RNAi. ego-1 interacts genetically with him-17, another regulator of chromatin and meiosis, to promote germline development. We conclude that EGO-1 is an essential component of meiotic silencing in C. elegans.
Figures
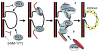
Similar articles
-
Regulation of heterochromatin assembly on unpaired chromosomes during Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis by components of a small RNA-mediated pathway.PLoS Genet. 2009 Aug;5(8):e1000624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000624. Epub 2009 Aug 28. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19714217 Free PMC article.
-
EGO-1, a putative RNA-directed RNA polymerase, promotes germline proliferation in parallel with GLP-1/notch signaling and regulates the spatial organization of nuclear pore complexes and germline P granules in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2005 Jul;170(3):1121-32. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.042135. Epub 2005 May 23. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15911573 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010;282:91-134. doi: 10.1016/S1937-6448(10)82002-7. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20630467 Review.
-
C. elegans RNA-dependent RNA polymerases rrf-1 and ego-1 silence Drosophila transgenes by differing mechanisms.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Apr;70(8):1469-81. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1218-8. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23224429 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi (Nematodes: Caenorhabditis elegans).Adv Genet. 2002;46:339-60. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(02)46012-9. Adv Genet. 2002. PMID: 11931230 Review.
Cited by
-
On the origin and functions of RNA-mediated silencing: from protists to man.Curr Genet. 2006 Aug;50(2):81-99. doi: 10.1007/s00294-006-0078-x. Epub 2006 May 12. Curr Genet. 2006. PMID: 16691418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNAi pathways contribute to developmental history-dependent phenotypic plasticity in C. elegans.RNA. 2013 Mar;19(3):306-19. doi: 10.1261/rna.036418.112. Epub 2013 Jan 17. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23329696 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic H3K9me2 distribution is influenced by the ALG-3 and ALG-4 pathway and by poly(U) polymerase activity.MicroPubl Biol. 2021 Sep 14;2021:10.17912/micropub.biology.000455. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000455. eCollection 2021. MicroPubl Biol. 2021. PMID: 34549171 Free PMC article.
-
ELLI-1, a novel germline protein, modulates RNAi activity and P-granule accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2017 Feb 9;13(2):e1006611. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006611. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28182654 Free PMC article.
-
Global effects of the CSR-1 RNA interference pathway on the transcriptional landscape.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Apr;21(4):358-65. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2801. Epub 2014 Mar 30. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24681887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matzke MA, Birchler JA. RNAi-mediated pathways in the nucleus. Nat Genet. 2005;6:24–35. - PubMed
-
- Lee JT. Sex chromosome inactivation: the importance of pairing. Curr Biol. 2005;15:R249–R252. - PubMed
-
- Hynes MJ, Todd RB. Detection of unpaired DNA at meiosis results in RNA-mediated silencing. Bioessays. 2003;25:99–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

