BRAF mutation predicts sensitivity to MEK inhibition
- PMID: 16273091
- PMCID: PMC3306236
- DOI: 10.1038/nature04304
BRAF mutation predicts sensitivity to MEK inhibition
Abstract
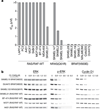
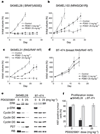
The kinase pathway comprising RAS, RAF, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) and extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) is activated in most human tumours, often through gain-of-function mutations of RAS and RAF family members. Using small-molecule inhibitors of MEK and an integrated genetic and pharmacologic analysis, we find that mutation of BRAF is associated with enhanced and selective sensitivity to MEK inhibition when compared to either 'wild-type' cells or cells harbouring a RAS mutation. This MEK dependency was observed in BRAF mutant cells regardless of tissue lineage, and correlated with both downregulation of cyclin D1 protein expression and the induction of G1 arrest. Pharmacological MEK inhibition completely abrogated tumour growth in BRAF mutant xenografts, whereas RAS mutant tumours were only partially inhibited. These data suggest an exquisite dependency on MEK activity in BRAF mutant tumours, and offer a rational therapeutic strategy for this genetically defined tumour subtype.
Figures


Comment in
-
Cancer biology: signatures guide drug choice.Nature. 2006 Jan 19;439(7074):274-5. doi: 10.1038/439274a. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16421553 No abstract available.
References
-
- Davies H, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–954. - PubMed
-
- Brose MS, et al. BRAF and RAS mutations in human lung cancer and melanoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6997–7000. - PubMed
-
- Gorden A, et al. Analysis of BRAF and N-RAS mutations in metastatic melanoma tissues. Cancer Res. 2003;63:3955–3957. - PubMed
-
- Crews CM, Alessandrini A, Erikson RL. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992;258:478–480. - PubMed
-
- Sebolt-Leopold JS, et al. Blockade of the MAP kinase pathway suppresses growth of colon tumors in vivo. Nature Med. 1999;5:810–816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

