Sequential analysis of surfactant, lung function and inflammation in cystic fibrosis patients
- PMID: 16274485
- PMCID: PMC1308867
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-133
Sequential analysis of surfactant, lung function and inflammation in cystic fibrosis patients
Abstract
Background: In a cross-sectional analysis of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients with mild lung disease, reduced surfactant activity was correlated to increased neutrophilic airway inflammation, but not to lung function. So far, longitudinal measurements of surfactant function in CF patients are lacking and it remains unclear how these alterations relate to the progression of airway inflammation as well as decline in pulmonary function over time.
Methods: As part of the BEAT trial, a longitudinal study to assess the course of airway inflammation in CF, we studied lung function, surfactant function and endobronchial inflammation using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from 20 CF patients with normal pulmonary function (median FEV1 94% of predicted) at three times over a three year period.
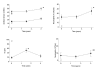
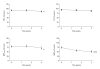
Results: There was a progressive loss of surfactant function, assessed as minimal surface tension. The decline in surfactant function was negatively correlated to an increase in neutrophilic inflammation and a decrease in lung function, assessed by FEV1, MEF(75/25%VC), and MEF(25%VC). The concentrations of the surfactant specific proteins A, C and D did not change, whereas SP-B increased during this time period.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest a link between loss of surfactant function driven by progressive airway inflammation and loss of small airway function in CF patients with limited lung disease.
Figures



References
-
- Enhorning G. Pulmonary surfactant function in alveoli and conducting airways. Can Respir J. 1996;3:21–27.
-
- Griese M. Pulmonary surfactant in health and lung diseases: state of the art. Eur Respir J. 1999;13:1455–1476. - PubMed
-
- Mander A, Langton-Hewer S, Bernhard W, Warner JO, Postle AD. Altered phospholipid composition and aggregate structure of lung surfactant is associated with impaired lung function in young children with respiratory infections. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002;27:714–721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

