CaMKII tethers to L-type Ca2+ channels, establishing a local and dedicated integrator of Ca2+ signals for facilitation
- PMID: 16275756
- PMCID: PMC1343528
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200505155
CaMKII tethers to L-type Ca2+ channels, establishing a local and dedicated integrator of Ca2+ signals for facilitation
Abstract
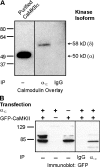
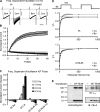
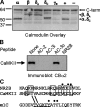
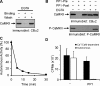
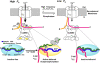
Ca2+-dependent facilitation (CDF) of voltage-gated calcium current is a powerful mechanism for up-regulation of Ca2+ influx during repeated membrane depolarization. CDF of L-type Ca2+ channels (Ca(v)1.2) contributes to the positive force-frequency effect in the heart and is believed to involve the activation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII). How CaMKII is activated and what its substrates are have not yet been determined. We show that the pore-forming subunit alpha(1C) (Ca(v)alpha1.2) is a CaMKII substrate and that CaMKII interaction with the COOH terminus of alpha1C is essential for CDF of L-type channels. Ca2+ influx triggers distinct features of CaMKII targeting and activity. After Ca2+-induced targeting to alpha1C, CaMKII becomes tightly tethered to the channel, even after calcium returns to normal levels. In contrast, activity of the tethered CaMKII remains fully Ca2+/CaM dependent, explaining its ability to operate as a calcium spike frequency detector. These findings clarify the molecular basis of CDF and demonstrate a novel enzymatic mechanism by which ion channel gating can be modulated by activity.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson, M., A. Braun, H. Schulman, and B. Premack. 1994. Multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase mediates Ca2+-induced enhancement of the L-type Ca2+ current in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Circ. Res. 75:854–861. - PubMed
-
- Bayer, K.U., P. De Koninck, A.S. Leonard, J.W. Hell, and H. Schulman. 2001. Interaction with the NMDA receptor locks CaMKII in an active conformation. Nature. 411:801–805. - PubMed
-
- Bence-Hanulec, K.K., J. Marshall, and L.A. Blair. 2000. Potentiation of neuronal L calcium channels by IGF-1 requires phosphorylation of the α1 subunit on a specific tyrosine residue. Neuron. 27:121–131. - PubMed
-
- Bradley, J., and S. Finkbeiner. 2002. An evaluation of specificity in activity-dependent gene expression in neurons. Prog. Neurobiol. 67:469–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

