Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8A catalyzes release of Galphai-GTP and nuclear mitotic apparatus protein (NuMA) from NuMA/LGN/Galphai-GDP complexes
- PMID: 16275912
- PMCID: PMC1283842
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508306102
Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8A catalyzes release of Galphai-GTP and nuclear mitotic apparatus protein (NuMA) from NuMA/LGN/Galphai-GDP complexes
Abstract
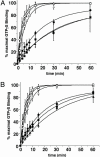
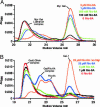
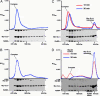
Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase (Ric) 8A is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor that activates certain G protein alpha-subunits. Genetic studies in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster have placed RIC-8 in a previously uncharacterized G protein signaling pathway that regulates centrosome movements during cell division. Components of this pathway include G protein subunits of the Galphai class, GPR or GoLoco domain-containing proteins, RGS (regulator of G protein signaling) proteins, and accessory factors. These proteins interact to regulate microtubule pulling forces during mitotic movement of chromosomes. It is unclear how the GTP-binding and hydrolysis cycle of Galphai functions in the context of this pathway. In mammals, the GoLoco domain-containing protein LGN (GPSM2), the LGN- and microtubule-binding nuclear mitotic apparatus protein (NuMA), and Galphai regulate a similar process. We find that mammalian Ric-8A dissociates Galphai-GDP/LGN/NuMA complexes catalytically, releasing activated Galphai-GTP in vitro. Ric-8A-stimulated activation of Galphai caused concomitant liberation of NuMA from LGN. We conclude that Ric-8A efficiently utilizes GoLoco/Galphai-GDP complexes as substrates in vitro and suggest that Ric-8A-stimulated release of Galphai-GTP and/or NuMA regulates the microtubule pulling forces on centrosomes during cell division.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

