GM-CSF action in the CNS decreases food intake and body weight
- PMID: 16276414
- PMCID: PMC1265876
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI25681
GM-CSF action in the CNS decreases food intake and body weight
Abstract
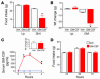
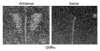
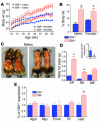
Many proinflammatory cytokines, such as leptin, play key roles in dynamic regulation of energy expenditure and food intake. The present work tested a role for the proinflammatory cytokine GM-CSF. Central but not peripheral administration of GM-CSF to adult rats significantly decreased food intake and body weight for at least 48 hours. Similar results were observed following central administration of GM-CSF in mice. GM-CSF receptor immunoreactivity was found on neurons within the paraventricular and arcuate nuclei of the hypothalamus. GM-CSF-deficient (GM-/-) mice weighed more and had significantly higher total body fat than wild-type (GM+/+) mice. Energy expenditure in GM-/- mice was decreased compared with that in GM+/+ mice. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that GM-CSF signaling in the CNS can regulate energy homeostasis.
Figures





References
-
- Friedman JM. The function of leptin in nutrition, weight, and physiology. Nutr. Rev. 2002;60:S1–S14; discussion S68–S84, 85–17. - PubMed
-
- Glaspy JA. Hematopoietic management in oncology practice. Part 1. Myeloid growth factors. Oncology (Williston Park). 2003;17:1593–1603. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton JA. GM-CSF in inflammation and autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2002;23:403–408. - PubMed
-
- La Cava A, Alviggi C, Matarese G. Unraveling the multiple roles of leptin in inflammation and autoimmunity. J. Mol. Med. 2004;82:4–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

