Effect of a small molecule inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear translocation in a murine model of arthritis and cultured human synovial cells
- PMID: 16277688
- PMCID: PMC1297584
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1834
Effect of a small molecule inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear translocation in a murine model of arthritis and cultured human synovial cells
Abstract
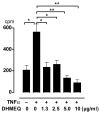
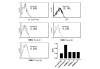
A small cell-permeable compound, dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin (DHMEQ), does not inhibit phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaB (inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB [NF-kappaB]) but selectively inhibits nuclear translocation of activated NF-kappaB. This study aimed to demonstrate the antiarthritic effect of this novel inhibitor of the NF-kappaB pathway in vivo in a murine arthritis model and in vitro in human synovial cells. Collagen-induced arthritis was induced in mice, and after onset of arthritis the mice were treated with DHMEQ (5 mg/kg body weight per day). Using fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS) cell lines established from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), NF-kappaB activity was examined by electrophoretic mobility shift assays. The expression of molecules involved in RA pathogenesis was determined by RT-PCR, ELISA, and flow cytometry. The proliferative activity of the cells was estimated with tritiated thymidine incorporation. After 14 days of treatment with DHMEQ, mice with collagen-induced arthritis exhibited decreased severity of arthritis, based on the degree of paw swelling, the number of swollen joints, and radiographic and histopathologic scores, compared with the control mice treated with vehicle alone. In RA FLS stimulated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha, activities of NF-kappaB components p65 and p50 were inhibited by DHMEQ, leading to suppressed expression of the key inflammatory cytokine IL-6, CC chemokine ligand-2 and -5, matrix metalloproteinase-3, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. The proliferative activity of the cells was also suppressed. This is the first demonstration of an inhibitor of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation exhibiting a therapeutic effect on established murine arthritis, and suppression of inflammatory mediators in FLS was thought to be among the mechanisms underlying such an effect.
Figures





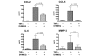
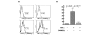

Similar articles
-
NF-kappaB inhibitor dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin suppresses osteoclastogenesis and expression of NFATc1 in mouse arthritis without affecting expression of RANKL, osteoprotegerin or macrophage colony-stimulating factor.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(5):R97. doi: 10.1186/ar2298. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 17892600 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of nuclear factor kappaB Pathways by dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, a novel inhibitor of breast carcinomas: antitumor and antiangiogenic potential in vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Feb 1;11(3):1287-93. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15709200
-
Suppression of diabetes-induced retinal inflammation by blocking the angiotensin II type 1 receptor or its downstream nuclear factor-kappaB pathway.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Sep;48(9):4342-50. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-1473. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17724226
-
Reversal of resistance to cytotoxic cancer therapies: DHMEQ as a chemo-sensitizing and immuno-sensitizing agent.Drug Resist Updat. 2007 Feb-Apr;10(1-2):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2007.01.002. Epub 2007 Feb 15. Drug Resist Updat. 2007. PMID: 17306602 Review.
-
Antitumor effect of a novel nuclear factor-kappa B activation inhibitor in bladder cancer cells.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2003 Dec;3(6):793-8. doi: 10.1586/14737140.3.6.793. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2003. PMID: 14686701 Review.
Cited by
-
Geniposide Suppresses Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Rat Chondrocytes via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2018 Mar;41(2):390-399. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0694-2. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29214554
-
Small molecules to the rescue: Inhibition of cytokine signaling in immune-mediated diseases.J Autoimmun. 2017 Dec;85:20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Jul 1. J Autoimmun. 2017. PMID: 28676205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arctigenin prevents the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB axis: In vitro and in vivo studies.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Apr;24(7):4183-4193. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15079. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32090454 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin (DHMEQ) can suppress tumour necrosis factor-α production in lipopolysaccharide-injected mice, resulting in rescuing mice from death in vivo.Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 Nov;166(2):299-306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04475.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21985376 Free PMC article.
-
DHMEQ, a novel nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor, induces selective depletion of alloreactive or phytohaemagglutinin-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells, decreases production of T helper type 1 cytokines, and blocks maturation of dendritic cells.Immunology. 2008 Jun;124(2):198-205. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02755.x. Epub 2008 Jan 23. Immunology. 2008. PMID: 18217958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Handel ML, McMorrow LB, Gravallese EM. Nuclear factor-κB in rheumatoid synovium. Localization of p50 and p65. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1762–1770. - PubMed
-
- Marok R, Winyard PG, Coumbe A, Kus ML, Gaffney K, Blades S, Mapp PI, Morris CJ, Blake DR, Kaltschmidt C, Baeuerle PA. Activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB in human inflamed synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39:583–591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

