Identification of citrullinated alpha-enolase as a candidate autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 16277695
- PMCID: PMC1297593
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1845
Identification of citrullinated alpha-enolase as a candidate autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
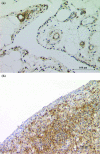
Antibodies against citrullinated proteins are highly specific for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but little is understood about their citrullinated target antigens. We have detected a candidate citrullinated protein by immunoblotting lysates of monocytic and granulocytic HL-60 cells treated with peptidylarginine deiminase. In an initial screen of serum samples from four patients with RA and one control, a protein of molecular mass 47 kDa from monocytic HL-60s reacted with sera from the patients, but not with the serum from the control. Only the citrullinated form of the protein was recognised. The antigen was identified by tandem mass spectrometry as alpha-enolase, and the positions of nine citrulline residues in the sequence were determined. Serum samples from 52 patients with RA and 40 healthy controls were tested for presence of antibodies against citrullinated and non-citrullinated alpha-enolase by immunoblotting of the purified antigens. Twenty-four sera from patients with RA (46%) reacted with citrullinated alpha-enolase, of which seven (13%) also recognised the non-citrullinated protein. Six samples from the controls (15%) reacted with both forms. Alpha-enolase was detected in the RA joint, where it co-localised with citrullinated proteins. The presence of antibody together with expression of antigen within the joint implicates citrullinated alpha-enolase as a candidate autoantigen that could drive the chronic inflammatory response in RA.
Figures

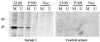




References
-
- Mageed RA. The RF antigen. In: van Venrooij WJ, Maini RN, editor. Manual of Biological Markers of Disease. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishing; 1996. pp. 1–27.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

