Science review: carnitine in the treatment of valproic acid-induced toxicity - what is the evidence?
- PMID: 16277730
- PMCID: PMC1297603
- DOI: 10.1186/cc3742
Science review: carnitine in the treatment of valproic acid-induced toxicity - what is the evidence?
Abstract
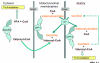
Valproic acid (VPA) is a broad-spectrum antiepileptic drug and is usually well tolerated, but rare serious complications may occur in some patients receiving VPA chronically, including haemorrhagic pancreatitis, bone marrow suppression, VPA-induced hepatotoxicity (VHT) and VPA-induced hyperammonaemic encephalopathy (VHE). Some data suggest that VHT and VHE may be promoted by carnitine deficiency. Acute VPA intoxication also occurs as a consequence of intentional or accidental overdose and its incidence is increasing, because of use of VPA in psychiatric disorders. Although it usually results in mild central nervous system depression, serious toxicity and even fatal cases have been reported. Several studies or isolated clinical observations have suggested the potential value of oral L-carnitine in reversing carnitine deficiency or preventing its development as well as some adverse effects due to VPA. Carnitine supplementation during VPA therapy in high-risk patients is now recommended by some scientific committees and textbooks, especially paediatricians. L-carnitine therapy could also be valuable in those patients who develop VHT or VHE. A few isolated observations also suggest that L-carnitine may be useful in patients with coma or in preventing hepatic dysfunction after acute VPA overdose. However, these issues deserve further investigation in controlled, randomized and probably multicentre trials to evaluate the clinical value and the appropriate dosage of L-carnitine in each of these conditions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Carnitine in the treatment of valproic acid-induced toxicity.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2009 Feb;47(2):101-11. doi: 10.1080/15563650902752376. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2009. PMID: 19280426 Review.
-
Two cases of valproic acid poisoning treated with L-carnitine.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2007 Dec;26(12):967-9. doi: 10.1177/0960327107087799. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 18375641
-
Effect of L-carnitine supplementation on acute valproate intoxication.Epilepsia. 1996 Jul;37(7):687-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1996.tb00634.x. Epilepsia. 1996. PMID: 8681902
-
A case of hemoperfusion and L-carnitine management in valproic acid overdose.Am J Emerg Med. 2008 Mar;26(3):388.e3-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2007.07.032. Am J Emerg Med. 2008. PMID: 18358983
-
[The decreased level of plasma carnitine in patients with epilepsy].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2017;117(6):106-110. doi: 10.17116/jnevro201711761106-110. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2017. PMID: 28745680 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Personalised therapeutic management of epileptic patients guided by pathway-driven breath metabolomics.Commun Med (Lond). 2021 Aug 2;1:21. doi: 10.1038/s43856-021-00021-3. eCollection 2021. Commun Med (Lond). 2021. PMID: 35602217 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperammonemia associated with valproic acid concentrations.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:217269. doi: 10.1155/2014/217269. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24868521 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolite profiling of whole murine embryos reveals metabolic perturbations associated with maternal valproate-induced neural tube closure defects.Birth Defects Res. 2017 Jan 30;109(2):106-119. doi: 10.1002/bdra.23583. Birth Defects Res. 2017. PMID: 27860192 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a survivor of valproate-induced acute liver failure: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2013 May 31;7:144. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-7-144. J Med Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23724918 Free PMC article.
-
Carbapenems as Antidotes for the Management of Acute Valproic Acid Poisoning.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 17;17(2):257. doi: 10.3390/ph17020257. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bedry R, Parrot F. Severe valproate poisoning [in French] Réanimation. 2004;13:324–333. doi: 10.1016/j.reaurg.2004.03.014. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

