Clinical review: role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 during sepsis
- PMID: 16277737
- PMCID: PMC1297602
- DOI: 10.1186/cc3732
Clinical review: role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 during sepsis
Abstract
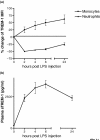
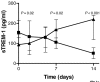
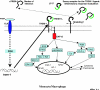
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM)-1 is a recently identified molecule that is involved in monocytic activation and in the inflammatory response. It belongs to a family related to the natural killer cell receptors and is expressed on neutrophils, mature monocytes and macrophages. The inflammatory response mediated by Toll-like receptor-2 and -4 stimulation is amplified by the engagement of TREM-1. The expression of membrane-bound TREM-1 is greatly increased on monocytes during sepsis. Moreover, infection induces the release of a soluble form of this receptor, which can be measured in biological fluid and may be useful as a diagnostic tool. Modulation of the TREM-1 signalling pathway by the use of small synthetic peptides confers interesting survival advantages during experimental septic shock in mice, even when this teatment is administered late after the onset of sepsis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells and the diagnosis of pneumonia and severe sepsis.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006 Feb;27(1):29-33. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-933671. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 16508879 Review.
-
The therapeutic potential of TREM-1 modulation in the treatment of sepsis and beyond.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006 May;7(5):438-42. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16729720
-
Intervention of an inflammation amplifier, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1, for treatment of autoimmune arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Jun;60(6):1615-23. doi: 10.1002/art.24554. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19479878
-
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell 1.Crit Care Clin. 2011 Apr;27(2):265-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2010.12.006. Crit Care Clin. 2011. PMID: 21440201
-
Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells (TREM) family and the application of its antagonists.Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2009 Jan;4(1):51-6. doi: 10.2174/157489109787236292. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2009. PMID: 19149696 Review.
Cited by
-
Significance of soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 elevation in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with sepsis.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Oct 12;16(1):559. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1893-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27729010 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of clinical sepsis-associated biomarkers in a septic mouse model.J Int Med Res. 2018 Jun;46(6):2410-2422. doi: 10.1177/0300060518764717. Epub 2018 Apr 12. J Int Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29644918 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of sepsis.Infect Chemother. 2014 Mar;46(1):1-12. doi: 10.3947/ic.2014.46.1.1. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Infect Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24693464 Free PMC article.
-
Use of high-dose nandrolone aggravates septic shock in a mouse model.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2011 Jun;27(6):222-9. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2010.12.015. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21601167 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of IL-6 and sTREM-1 in SIRS and Sepsis in Children.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Jun 22;2020:8201585. doi: 10.1155/2020/8201585. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32655314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouchon A, Dietrich J, Colonna M. Cutting edge: Inflammatory responses can be triggered by TREM-1, a novel receptor expressed on neutrophils and monocytes. J Immunol. 2000;164:4991–4995. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

