Chromatin and siRNA pathways cooperate to maintain DNA methylation of small transposable elements in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 16277745
- PMCID: PMC1297646
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-11-r90
Chromatin and siRNA pathways cooperate to maintain DNA methylation of small transposable elements in Arabidopsis
Abstract
Background: DNA methylation occurs at preferred sites in eukaryotes. In Arabidopsis, DNA cytosine methylation is maintained by three subfamilies of methyltransferases with distinct substrate specificities and different modes of action. Targeting of cytosine methylation at selected loci has been found to sometimes involve histone H3 methylation and small interfering (si)RNAs. However, the relationship between different cytosine methylation pathways and their preferred targets is not known.
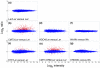
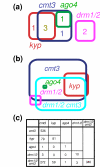
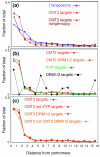
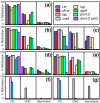
Results: We used a microarray-based profiling method to explore the involvement of Arabidopsis CMT3 and DRM DNA methyltransferases, a histone H3 lysine-9 methyltransferase (KYP) and an Argonaute-related siRNA silencing component (AGO4) in methylating target loci. We found that KYP targets are also CMT3 targets, suggesting that histone methylation maintains CNG methylation genome-wide. CMT3 and KYP targets show similar proximal distributions that correspond to the overall distribution of transposable elements of all types, whereas DRM targets are distributed more distally along the chromosome. We find an inverse relationship between element size and loss of methylation in ago4 and drm mutants.
Conclusion: We conclude that the targets of both DNA methylation and histone H3K9 methylation pathways are transposable elements genome-wide, irrespective of element type and position. Our findings also suggest that RNA-directed DNA methylation is required to silence isolated elements that may be too small to be maintained in a silent state by a chromatin-based mechanism alone. Thus, parallel pathways would be needed to maintain silencing of transposable elements.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Locus-specific control of DNA methylation by the Arabidopsis SUVH5 histone methyltransferase.Plant Cell. 2006 May;18(5):1166-76. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.041400. Epub 2006 Mar 31. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 16582009 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNAs prevent transcription-coupled loss of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002350. Epub 2011 Oct 27. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22046144 Free PMC article.
-
ARGONAUTE4 control of locus-specific siRNA accumulation and DNA and histone methylation.Science. 2003 Jan 31;299(5607):716-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1079695. Epub 2003 Jan 9. Science. 2003. PMID: 12522258
-
Silencing of transposons in plant genomes: kick them when they're down.Genome Biol. 2004;5(12):249. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-12-249. Epub 2004 Nov 16. Genome Biol. 2004. PMID: 15575975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and mechanism of histone methylation dynamics in Arabidopsis.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2022 Jun;67:102211. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102211. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35452951 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic silencing of clustered tRNA genes in Arabidopsis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Oct 9;48(18):10297-10312. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa766. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32941623 Free PMC article.
-
SDG714, a histone H3K9 methyltransferase, is involved in Tos17 DNA methylation and transposition in rice.Plant Cell. 2007 Jan;19(1):9-22. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.048124. Epub 2007 Jan 26. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17259261 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of methylation-mediated transcriptional gene silencing by βC1-SAHH protein interaction during geminivirus-betasatellite infection.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002329. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002329. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22028660 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Chromatin Regulators Reveals Specific Features of Rice DNA Methylation Pathways.Plant Physiol. 2016 Jul;171(3):2041-54. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00393. Epub 2016 May 12. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27208249 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput sequencing of Arabidopsis microRNAs: evidence for frequent birth and death of MIRNA genes.PLoS One. 2007 Feb 14;2(2):e219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000219. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17299599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen T, Li E. Structure and function of eukaryotic DNA methyltransferases. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2004;60:55–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

