Systematic discovery of new recognition peptides mediating protein interaction networks
- PMID: 16279839
- PMCID: PMC1283537
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030405
Systematic discovery of new recognition peptides mediating protein interaction networks
Abstract
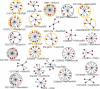
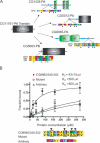
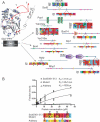
Many aspects of cell signalling, trafficking, and targeting are governed by interactions between globular protein domains and short peptide segments. These domains often bind multiple peptides that share a common sequence pattern, or "linear motif" (e.g., SH3 binding to PxxP). Many domains are known, though comparatively few linear motifs have been discovered. Their short length (three to eight residues), and the fact that they often reside in disordered regions in proteins makes them difficult to detect through sequence comparison or experiment. Nevertheless, each new motif provides critical molecular details of how interaction networks are constructed, and can explain how one protein is able to bind to very different partners. Here we show that binding motifs can be detected using data from genome-scale interaction studies, and thus avoid the normally slow discovery process. Our approach based on motif over-representation in non-homologous sequences, rediscovers known motifs and predicts dozens of others. Direct binding experiments reveal that two predicted motifs are indeed protein-binding modules: a DxxDxxxD protein phosphatase 1 binding motif with a KD of 22 microM and a VxxxRxYS motif that binds Translin with a KD of 43 microM. We estimate that there are dozens or even hundreds of linear motifs yet to be discovered that will give molecular insight into protein networks and greatly illuminate cellular processes.
Figures


References
-
- Poglitsch CL, Meredith GD, Gnatt AL, Jensen GJ, Chang WH, et al. Electron crystal structure of an RNA polymerase II transcription elongation complex. Cell. 1999;98:791–798. - PubMed
-
- Jeffrey PD, Russo AA, Polyak K, Gibbs E, Hurwitz J, et al. Mechanism of CDK activation revelated by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex. Nature. 1995;376:313–320. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T, Scott JD. Signaling through scaffold, anchoring, and adaptor proteins. Science. 1997;278:2075–2080. - PubMed
-
- Sudol M. From Src Homology domains to other signaling modules: Proposal of the ‘protein recognition code'. Oncogene. 1998;17:1469–1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

