Genetic polymorphisms in human SULT1A1 and UGT1A1 genes associate with breast tumor characteristics: a case-series study
- PMID: 16280036
- PMCID: PMC1410736
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr1318
Genetic polymorphisms in human SULT1A1 and UGT1A1 genes associate with breast tumor characteristics: a case-series study
Abstract
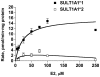
Introduction: Estrogens are important in breast cancer development. SULT1A1 and UGT1A1 catalyze estrogen metabolism and are polymorphic. The SULT1A1*2 protein exhibits low activity, and a TA repeat within the UGT1A1 promoter alters the level of expression of the protein. We hypothesized that the SULT1A1*2 allozyme has decreased capacity to sulfate estrogens, that the SULT1A1*2 allele conferred increased capacity of cells to proliferate in response to estrogens, and that individuals with the variant SULT1A1 and UGT1A1 genotypes exhibited different breast tumor characteristics.
Methods: The capacity for SULT1A1*2 to sulfate 17beta-estradiol and the capacity for cells expressing SULT1A1*1 or SULT1A1*2 to proliferate in response to 17beta-estradiol was evaluated. A case-series study was performed in a total of 210 women with incident breast cancer, including 177 Caucasians, 25 African-Americans and eight women of other ethnic background. The SULT1A1 and UGT1A1 genotypes were determined and a logistic regression model was used to analyze genotype-phenotype associations.
Results: We determined that the SULT1A1*1/*1 high-activity genotype was associated with tumor size <or=2 cm (odds ratio = 2.63, 95% confidence interval = 1.25-5.56, P = 0.02). Individuals with low-activity UGT1A1 genotypes (UGT1A1*28/*28 or UGT1A1*28/*34) were more likely to have an age at diagnosis >or=60 years (odds ratio = 3.70, 95% confidence interval = 1.33-10.00, P = 0.01). Individuals with both SULT1A1 and UGT1A1 high-activity genotypes had low tumor grade (odds ratio = 2.56, 95% confidence interval = 1.04-6.25, P = 0.05). Upon stratification by estrogen receptor status, significant associations were observed predominantly in estrogen receptor-negative tumors.
Conclusion: The data suggest that genetic variation in SULT1A1 and UGT1A1 may influence breast cancer characteristics and might be important for breast cancer prognosis.
Figures

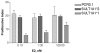
References
-
- Raftogianis R, Creveling C, Weinshilboum R, Weisz J. Estrogen metabolism by conjugation. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2000;27:113–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

