Reduction of D-dimer levels after therapeutic administration of antithrombin in acquired antithrombin deficiency of severe sepsis
- PMID: 16280058
- PMCID: PMC1414038
- DOI: 10.1186/cc3808
Reduction of D-dimer levels after therapeutic administration of antithrombin in acquired antithrombin deficiency of severe sepsis
Abstract
Introduction: In acute disseminated intravascular coagulation, the effect of antithrombin (AT) administration on elevated levels of D-dimer is not well established. In the present study, we report on changes in circulating levels of D-dimer in response to administration of AT in a series of patients with acquired AT deficiency due to severe sepsis.
Methods: Eight consecutive critically ill medical patients presenting with acute disseminated intravascular coagulation associated with severe sepsis/septic shock received a single bolus infusion of AT over 30 minutes, aiming to achieve physiological AT levels. Haemostatic parameters including D-dimer were assessed prior to, 6 and 24 h after AT administration. An average of 42 +/- 9 U/kg body weight was infused.
Results: Following AT substitution, elevated levels of D-dimer fell whereas AT levels rose.
Conclusion: These observations support the notion that AT can favourably affect fibrin degradation accompanying disseminated intravascular coagulation of severe sepsis.
Figures
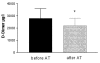
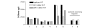
Comment in
-
Antithrombin in sepsis revisited.Crit Care. 2005;9(6):624-5. doi: 10.1186/cc3819. Epub 2005 Sep 26. Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 16356248 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Antithrombin in sepsis revisited.Crit Care. 2005;9(6):624-5. doi: 10.1186/cc3819. Epub 2005 Sep 26. Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 16356248 Free PMC article.
-
[Coagulation tests in septic surgical patients].Acta Med Croatica. 2004;58(5):389-94. Acta Med Croatica. 2004. PMID: 15756805 Croatian.
-
International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis score for overt disseminated intravascular coagulation predicts organ dysfunction and fatality in sepsis patients.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2006 Sep;17(6):445-51. doi: 10.1097/01.mbc.0000240916.63521.2e. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2006. PMID: 16905947
-
Antithrombin substitution therapy.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998 Nov;9 Suppl 3:S17-21; discussion S21-2. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998. PMID: 10102495 Review.
-
Antithrombin replacement in patients with sepsis and septic shock.Haematologica. 1999 May;84(5):452-60. Haematologica. 1999. PMID: 10329925 Review.
Cited by
-
A latent class approach for sepsis diagnosis supports use of procalcitonin in the emergency room for diagnosis of severe sepsis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2013 Sep 19;13(1):23. doi: 10.1186/1471-2253-13-23. BMC Anesthesiol. 2013. PMID: 24050481 Free PMC article.
-
Association between D-dimer-to-albumin ratio and 28-days all-cause mortality in patients with sepsis.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 16;14(1):28361. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79911-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39550487 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombocytopenia in Sepsis.Life (Basel). 2025 Feb 11;15(2):274. doi: 10.3390/life15020274. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recommendations for the use of antithrombin concentrates and prothrombin complex concentrates.Blood Transfus. 2009 Oct;7(4):325-34. doi: 10.2450/2009.0116-09. Blood Transfus. 2009. PMID: 20011645 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical review: molecular mechanisms underlying the role of antithrombin in sepsis.Crit Care. 2006 Feb;10(1):209. doi: 10.1186/cc4822. Crit Care. 2006. PMID: 16542481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Jonge E, Levi M, Stoutenbeek CP, van Deventer SJ. Current drug treatment strategies for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Drugs. 1998;55:767–777. - PubMed
-
- Eisele B, Lamy M, Thijs LG, Keinecke HO, Schuster HP, Matthias FR, Fourrier F, Heinrichs H, Delvos U. Antithrombin III in patients with severe sepsis. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind multicenter trial plus a meta-analysis on all randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials with antithrombin III in severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 1998;24:663–672. doi: 10.1007/s001340050642. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Warren BL, Eid A, Singer P, Pillay SS, Carl P, Novak I, Chalupa P, Atherstone A, Penzes I, Kubler A, et al. KyberSept Trial Study Group. Caring for the critically ill patient. High-dose antithrombin III in severe sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc. 2001;286:1869–1878. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.15.1869. - DOI - PubMed
-
- DePalo V, Kessler C, Opal SM. Success or failure in phase III sepsis trials: Comparisons between drotrecogin alpha (activated) and antithrombin III clinical trials. Adv Sepsis. 2001;1:114–124.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

