CysLT1 leukotriene receptor antagonists inhibit the effects of nucleotides acting at P2Y receptors
- PMID: 16280122
- PMCID: PMC4967539
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.10.003
CysLT1 leukotriene receptor antagonists inhibit the effects of nucleotides acting at P2Y receptors
Abstract
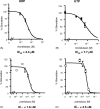
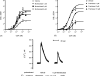
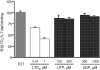
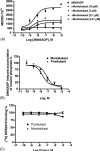
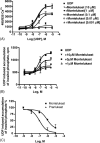
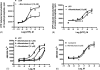
Montelukast and pranlukast are orally active leukotriene receptor antagonists selective for the CysLT1 receptor. Conversely, the hP2Y(1,2,4,6,11,12,13,14) receptors represent a large family of GPCRs responding to either adenine or uracil nucleotides, or to sugar-nucleotides. Montelukast and pranlukast were found to inhibit nucleotide-induced calcium mobilization in a human monocyte-macrophage like cell line, DMSO-differentiated U937 (dU937). Montelukast and pranlukast inhibited the effects of UTP with IC50 values of 7.7 and 4.3 microM, respectively, and inhibited the effects of UDP with IC50 values of 4.5 and 1.6 microM, respectively, in an insurmountable manner. Furthermore, ligand binding studies using [3H]LTD4 excluded the possibility of orthosteric nucleotide binding to the CysLT1 receptor. dU937 cells were shown to express P2Y2, P2Y4, P2Y6, P2Y11, P2Y13 and P2Y14 receptors. Therefore, these antagonists were studied functionally in a heterologous expression system for the human P2Y receptors. In 1321N1 astrocytoma cells stably expressing human P2Y(1,2,4,6) receptors, CysLT1 antagonists inhibited both the P2Y agonist-induced activation of phospholipase C and intracellular Ca2+ mobilization. IC50 values at P2Y1 and P2Y6 receptors were <1 microM. In control astrocytoma cells expressing an endogenous M3 muscarinic receptor, 10 microM montelukast had no effect on the carbachol-induced rise in intracellular Ca2+. These data demonstrated that CysLT1 receptor antagonists interact functionally with signaling pathways of P2Y receptors, and this should foster the study of possible implications for the clinical use of these compounds in asthma or in other inflammatory conditions.
Figures

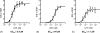
Similar articles
-
Differential inhibitory effects of CysLT(1) receptor antagonists on P2Y(6) receptor-mediated signaling and ion transport in human bronchial epithelia.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022363. Epub 2011 Jul 22. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21799837 Free PMC article.
-
CysLT1 receptor is a target for extracellular nucleotide-induced heterologous desensitization: a possible feedback mechanism in inflammation.J Cell Sci. 2005 Dec 1;118(Pt 23):5625-36. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02668. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16306225
-
Methanocarba modification of uracil and adenine nucleotides: high potency of Northern ring conformation at P2Y1, P2Y2, P2Y4, and P2Y11 but not P2Y6 receptors.J Med Chem. 2002 Jan 3;45(1):208-18. doi: 10.1021/jm010369e. J Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 11754592 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological profiles of cloned mammalian P2Y-receptor subtypes.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Jun;110(3):415-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.08.014. Epub 2005 Oct 28. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16257449 Review.
-
Molecular pharmacology of P2Y-receptors.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000 Nov;362(4-5):310-23. doi: 10.1007/s002100000310. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11111826 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast+Levocetirizine Combination Therapy Compared to Montelukast Monotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis in Children.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024 Nov;16(6):652-667. doi: 10.4168/aair.2024.16.6.652. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39622689 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy.Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):281-341. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.3.3. Pharmacol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16968944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosteric modulation of purine and pyrimidine receptors.Adv Pharmacol. 2011;61:187-220. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385526-8.00007-2. Adv Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21586360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential inhibitory effects of CysLT(1) receptor antagonists on P2Y(6) receptor-mediated signaling and ion transport in human bronchial epithelia.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022363. Epub 2011 Jul 22. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21799837 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteinyl leukotrienes acting via granule membrane-expressed receptors elicit secretion from within cell-free human eosinophil granules.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Feb;125(2):477-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.029. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20159258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Samuelsson B. Leukotrienes: mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science. 1983;220:568–75. - PubMed
-
- Dahlen SE, Hedqvist P, Hammarstrom S, Samuelsson B. Leukotrienes are potent constrictors of human bronchi. Nature. 1980;288:484–6. - PubMed
-
- Nicosia S, Capra V, Rovati GE. Leukotrienes as mediators of asthma. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2001;14:3–19. - PubMed
-
- Porreca E, Di Febbo C, Di Sciullo A, Angelucci D, Nasuti M, Vitullo P, et al. Cysteinyl leukotriene D4 induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation: a possible role in myointimal hyperplasia. Thromb Haemost. 1996;76:99–104. - PubMed
-
- Lotzer K, Spanbroek R, Hildner M, Urbach A, Heller R, Bretschneider E, et al. Differential leukotriene receptor expression and calcium responses in endothelial cells and macrophages indicate 5-lipoxygenase-dependent circuits of inflammation and atherogenesis. Arterioscl Throm Vas Biol. 2003;23:E32–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

