Relationships between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacteria causing nosocomial infections from 1991-2003 at a university hospital in Taiwan
- PMID: 16280243
- PMCID: PMC7126312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2005.08.016
Relationships between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacteria causing nosocomial infections from 1991-2003 at a university hospital in Taiwan
Abstract
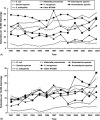
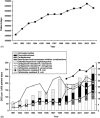
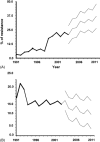
This study was conducted to evaluate the relationship between antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial use in a university hospital in Taiwan. Disk susceptibility data of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, Proteus spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp., Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and other non-fermentative Gram-negative bacilli causing nosocomial infections were evaluated. Data on annual patient-days and annual consumption (defined daily dose (DDD) per 1000 patient-days) of extended-spectrum cephalosporins (cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, flumoxef, cefepime and cefpirome), beta-lactam-beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations (ticarcillin/clavulanic acid and piperacillin/tazobactam), carbapenems (imipenem and meropenem), aminoglycosides (amikacin, gentamicin and tobramycin), fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin (oral and injectable) and oral levofloxacin and moxifloxacin) from 1991 to 2003 were analysed. Increasing trends of incidences of several of these bacteria causing all nosocomial infections or nosocomial bloodstream infections were noted from 1991 to 2003. The annual patient-days of the hospital significantly increased, from 360210 in 1991 to 672676 in 2002 (linear regression analysis, P < 0.05), but slightly decreased in 2003 (629168) owing to the severe acute respiratory syndrome epidemic in Taiwan. The rise in cefotaxime-resistant or ciprofloxacin-resistant E. coli and meropenem-resistant P. aeruginosa was significantly correlated with increased consumption of extended-spectrum cephalosporins, beta-lactam-beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations, carbapenems, fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides (for ciprofloxacin-resistant E. coli and meropenem-resistant P. aeruginosa only) in the hospital (Pearson's correlation coefficient, r > 0.72 (or < -0.72) and P-value < 0.05). Increased ciprofloxacin-resistant K. pneumoniae and meropenem-resistant Acinetobacter spp. was significantly associated with the increased usage of extended-spectrum cephalosporins but not with the other four classes of antibiotics. This 13-year study in a hospital demonstrated significant changes in antimicrobial use, which may have affected antimicrobial resistance in certain Gram-negative bacteria at the hospital.
Figures
References
-
- Archibald L., Phillips L., Monnet D. Antimicrobial resistance in isolates from inpatients and outpatients in the United States: increasing importance of the intensive care unit. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;24:211–215. - PubMed
-
- Rhomberg P.R., Jones R.N., Sader H.S. Results from the Meropenem Yearly Susceptibility Test Information Collection (MYSTIC) Programme: report of the 2001 data from 15 United States medical centres. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2004;23:52–59. - PubMed
-
- Sader H.S., Biedenbach D.J., Jones R.N. Global patterns of susceptibility for 21 commonly utilized antimicrobial agents tested against 48, 440 Enterobacteriaceae in the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (1997–2001) Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003;47:361–364. - PubMed
-
- Fridkin S.K., Steward C.D., Edwards J.R. Surveillance of antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in United States hospitals: project ICARE phase 2. Project Intensive Care Antimicrobial Resistance Epidemiology (ICARE) hospitals. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:245–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

